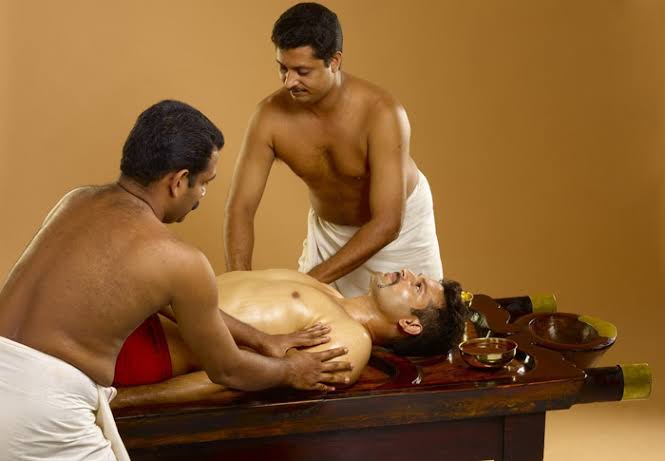
General Introduction Ayurvedic dermatology, as part of the ancient Indian healing system Ayurveda, provides a holistic approach to skincare. With over 5,000 years of history, Ayurveda treats the skin not just as an isolated organ but as an integral part of overall health and wellness. This comprehensive approach focuses on bringing balance to the entire body, mind, and spirit, which is believed to reflect outwardly as radiant and healthy skin. Fundamental Principles of Ayurvedic Dermatology In Ayurvedic philosophy, each person has a unique combination of three primary energies or doshas: Vata, Pitta, and Kapha. These doshas represent different elemental qualities: Vata (Air and Space): Governs movement and is associated with dry, rough, and thin skin. When Vata is imbalanced, it can result in dryness, dehydration, premature aging, and conditions like eczema. Pitta (Fire and Water): Relates to metabolism and is often associated with oily and sensitive skin. Pitta imbalances can lead to inflammatory skin conditions like acne, rosacea, rashes, and redness. Kapha (Earth and Water): Associated with structure and lubrication, Kapha generally produces thick, oily, and smooth skin. Excess Kapha can cause issues like excessive oiliness, clogged pores, and cystic acne. Ayurvedic dermatology aims to understand each individual’s unique doshic constitution (Prakriti) and current doshic imbalance (Vikriti). By identifying which dosha is out of balance, treatments can be customized to restore harmony, thereby promoting skin health. Key Components of Ayurvedic Dermatology 1. Herbal Remedies and Plant-Based Ingredients: Ayurveda utilizes a vast array of herbs and natural ingredients to address specific skin concerns. Some commonly used herbs include: – Turmeric: Known for its anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and antioxidant properties, turmeric is a popular remedy for acne and skin brightening. – Neem: Valued for its powerful antibacterial and antifungal properties, neem helps combat acne, eczema, and other skin infections. – Aloe Vera: Used to soothe and hydrate the skin, aloe vera is effective for sunburns, dryness, and irritation. – Sandalwood: Recognized for its cooling and anti-inflammatory effects, sandalwood is often used to treat Pitta-related skin issues like rashes and redness. – Manjistha (Indian Madder): Known for its blood-purifying properties, it helps in treating hyperpigmentation and supports even skin tone. Ayurvedic herbal treatments are typically applied in the form of pastes, powders, oils, or poultices directly on the skin or taken internally to promote overall wellness and detoxification. 2. Oil Massage (Abhyanga) and Skin Nourishment: Abhyanga is a daily self-massage practice with warm herbal oils. This technique is believed to nourish the skin, improve circulation, and eliminate toxins. The choice of oil is tailored to balance specific doshas: – Sesame Oil: Warm and grounding, this is beneficial for Vata dosha due to its deeply moisturizing properties. – Coconut Oil: Cooling and light, it is ideal for Pitta dosha to soothe sensitive skin and reduce inflammation. – Almond Oil: Gentle and moisturizing, it can support Kapha dosha by improving circulation without adding excess oiliness. Abhyanga not only rejuvenates the skin but also reduces stress, improves lymphatic drainage, and supports the body’s detoxification processes. 3. Diet and Nutritional Support for Skin Health: In Ayurveda, diet is integral to skin health. The Ayurvedic approach to nutrition focuses on consuming fresh, seasonal, and organic foods that support one’s doshic balance. Key dietary guidelines include: – Vata: Warm, moist, and grounding foods like cooked grains, root vegetables, and ghee help to counteract dryness and promote hydration. – Pitta: Cooling foods such as cucumbers, melons, leafy greens, and coconut water reduce internal heat and inflammation. – Kapha: Light, dry, and spicy foods like beans, greens, and ginger can help counterbalance oiliness and promote detoxification. Ayurveda also recommends avoiding processed foods, excessive sugar, and caffeine, as these can disrupt the doshas and lead to skin issues. Hydration with herbal teas and ample water intake is also emphasized to keep the skin moisturized and clear. 4. Detoxification and Panchakarma Therapy: Panchakarma, an Ayurvedic detoxification therapy, is central to maintaining healthy skin. This intensive cleansing process involves techniques like: – Swedana (Steam Therapy): Opens pores and encourages sweating to eliminate toxins. – Virechana (Herbal Laxatives): Helps cleanse the digestive system and liver, which is believed to improve skin clarity. – Nasya (Nasal Cleansing): Clears toxins from the respiratory system and head region, which can impact skin health. By purifying the body internally, Panchakarma can address chronic skin conditions such as acne, psoriasis, and eczema at their root cause. 5. Yoga, Meditation, and Breathwork (Pranayama): Stress is a significant factor in many skin conditions, and Ayurveda addresses this through mind-body practices. Yoga poses (asanas) that improve circulation and detoxification are recommended, along with meditation to reduce stress. Pranayama, or breathwork, helps in balancing the mind and body, promoting mental clarity, and improving oxygenation of the skin. 6. Natural Exfoliants, Cleansers, and Skin Rituals: Ayurvedic skincare incorporates gentle exfoliants and cleansers that avoid harsh chemicals. Common natural ingredients include: – Gram Flour (Besan): A mild exfoliant that can remove dead skin cells and brighten the complexion. – Honey: Naturally hydrating and antibacterial, honey helps cleanse and soften the skin. – Rose Water: Used as a toner to balance the skin’s pH, reduce redness, and refresh the complexion. Ayurvedic beauty rituals also involve herbal face masks, milk baths, and mud masks that draw out impurities, improve skin texture, and provide nourishment. Ayurvedic Approach to Specific Skin Conditions – Acne and Inflammation: For Pitta-related issues, Ayurvedic treatments include cooling and purifying herbs such as neem, turmeric, and sandalwood. Dietary modifications that limit spicy, oily, and acidic foods are recommended. – Dryness and Premature Aging: Often related to Vata imbalances, dryness is treated with nourishing oils and hydrating herbs. Internal treatments include consuming healthy fats and oils, while externally, abhyanga with sesame oil provides moisture and elasticity. – Hyperpigmentation and Uneven Skin Tone: Manjistha, turmeric, and licorice root are commonly used for hyperpigmentation. Regular application of these herbs, combined with antioxidant-rich foods, can help balance melanin production and brighten the complexion. The