Global Perspectives on Folliculitis: Ayurveda’s Approach to Prevention, Treatment, and Healthcare Disparities
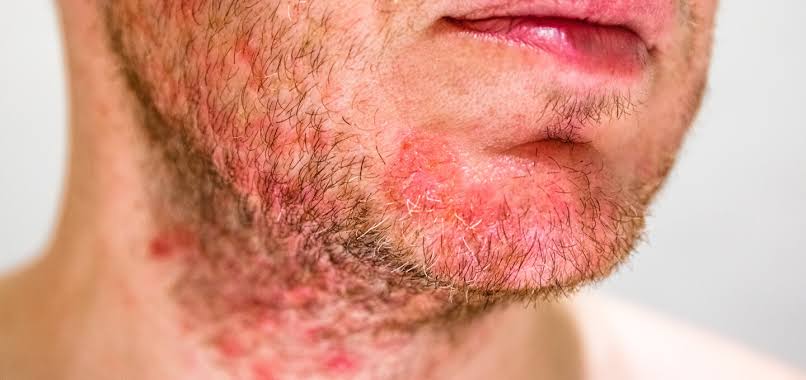
Folliculitis is an inflammation or infection of hair follicles, the tiny openings in the skin from which hair grows. It can occur anywhere on the body with hair, but it is most common on the face, scalp, arms, legs, and buttocks. It can be mild and self-limiting or severe, causing discomfort and complications if not treated. Symptoms of Folliculitis Early Signs:Small, red, or white bumps around hair follicles.Itchy or tender skin.Progression:Bumps may become pus-filled blisters.Skin redness or swelling around the follicle.Chronic or Severe Cases:Larger, painful boils or carbuncles.Scarring or dark spots (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation).Persistent itching, burning, or discomfort. Causes of Folliculitis Infections:- Other factors:- Classification of folliculitis Folliculitis can be categorized based on its cause and depth of infection. Here are the main types: 1. Superficial Folliculitis Affects only the upper part of the hair follicle. Common types: Bacterial Folliculitis: Caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Pseudomonas Folliculitis: Known as hot tub folliculitis, caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pityrosporum Folliculitis: Caused by yeast (Malassezia), often seen on the back, chest, and shoulders. 2. Deep Folliculitis Involves the entire follicle, including deeper layers of the skin. Common types: Sycosis Barbae: Chronic folliculitis of the beard area, often from shaving. Boils and Carbuncles: Severe bacterial infections leading to pus-filled lumps. Gram-Negative Folliculitis: Often occurs after long-term antibiotic treatment for acne. 3. Non-Infectious Folliculitis Caused by physical irritation or blocked hair follicles. Types include: Irritant Folliculitis: Due to friction, tight clothing, or excessive sweating. Eosinophilic Folliculitis: Seen in people with compromised immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS patients. Treatment and Herbal Remedies Internal Medications: Neem (Azadirachta indica): Known for antibacterial and antifungal properties, used as a decoction or in capsule form.Haridra (Turmeric): Blood purifier, anti-inflammatory, and useful in managing infections.Manjistha (Rubia cordifolia): Effective in skin detoxification and healing.Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia): Immunomodulator and useful in balancing Kapha and Pitta doshas.Triphala: A natural cleanser for the gut, supports detoxification. External Treatments Neem Oil: Apply on affected areas to reduce inflammation and bacterial growth.Aloe Vera Gel: Soothes irritation and promotes healing.Kumkumadi Tailam: For scars and pigmentation post-folliculitis. Panchakarma Therapies Virechana (Purgation Therapy): Removes excess Pitta dosha, aiding in skin health.Lepam: Application of herbal paste made from turmeric, sandalwood, and neem.Abhyanga (Oil Massage): With medicated oils like neem or nalpamaradi for better circulation. Dietary Guidelines • Avoid spicy, oily, and fermented foods.• Include bitter-tasting foods like karela (bitter gourd) and leafy greens.• Consume plenty of water and detoxifying herbal teas. Modern Treatment Modern treatments for folliculitis include a variety of medications, topical solutions, and procedures designed to reduce infection, inflammation, and recurrence. 1. Topical Treatments 2. Systemic Medications 3. Laser and Light Therapy 4. Drainage and Surgical Procedures 5. Additional Procedures Here’s a detailed explanation of the difference between Folliculitis and Carbuncle, along with an Ayurvedic perspective. Difference Between Folliculitis and Carbuncle Feature Folliculitis Carbuncle Definition Inflammation or infection of hair follicles, usually superficial. A deep-seated, painful infection of multiple hair follicles forming a pus-filled lump. Cause Mostly Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, fungi, viruses, or irritation from shaving, friction, or sweat. Caused by Staphylococcus aureus, often in people with weak immunity, diabetes, or poor hygiene. Appearance Small, red, pus-filled bumps around hair follicles, often itchy. Large, swollen, red, and painful lump with multiple pus-filled openings. Depth of Infection Superficial (affects the upper part of the hair follicle). Deep (spreads into the skin layers and underlying tissues). Pain & Tenderness Mild discomfort or itching. Severe pain, tenderness, and warmth. Spread & Contagiousness Can spread to nearby follicles but usually remains localized. Can spread deeper into tissues and may cause fever and fatigue. Healing Time Heals within a few days to weeks with proper care. Takes longer to heal (weeks), may require drainage and antibiotics. Treatment Antibacterial soaps, warm compresses, topical or oral antibiotics for bacterial cases. Requires medical attention, antibiotics, incision & drainage, and proper wound care. Self-Care Tips for Folliculitis • Keep the affected area clean and dry.• Use gentle, non-irritating cleansers.• Avoid tight clothing or rough fabrics that can irritate the skin.• Don’t share razors or personal items.• Avoid shaving over inflamed areas; instead, trim hair carefully if needed.• Use warm compresses to relieve pain and draw out pus.• Avoid hot tubs or pools if you are prone to infections. Maintain hygiene and manage diabetes with a proper diet (low in sugar and high in fiber).Avoid irritants like tight clothing. Frequently asked?? • What is folliculitis?It’s an infection or inflammation of hair follicles causing red, itchy, or pus-filled bumps.• What causes folliculitis?Bacteria, fungi, viruses, or irritation from shaving, tight clothing, or sweat.• Is folliculitis contagious?It can be, especially if caused by bacteria or fungi.• Can diabetes worsen folliculitis?Yes, diabetes slows healing and increases the risk of infection.• How is folliculitis treated in Ayurveda?Using herbs like neem, turmeric, and manjistha, detox therapies, and herbal pastes.• How to prevent folliculitis?Maintain hygiene, avoid tight clothing, and keep skin dry.• When should I see a doctor?If it’s recurrent, painful, or doesn’t heal in a few days.• Can folliculitis leave scars?Yes, if not treated properly or if it becomes severe, folliculitis can lead to scarring or hyperpigmentation.• Can I shave with folliculitis?It’s best to avoid shaving over inflamed areas to prevent further irritation. If you must shave, use a clean razor and avoid pressing too hard on the skin.• Is folliculitis the same as acne?No, though both involve clogged hair follicles, acne is primarily caused by excess oil and bacteria, while folliculitis is caused by infection or inflammation of the follicle.• What is the best way to treat folliculitis naturally?Using antimicrobial herbs like neem, turmeric, and aloe vera, while maintaining proper hygiene and diet to support the immune system.• Can I use over-the-counter treatments for folliculitis?Yes, topical treatments with benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid can help, but if the condition persists, a visit to a dermatologist is recommended.• Is there any dietary advice for preventing folliculitis?Yes, avoid excess sugar, spicy, or oily foods, and focus on a diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and foods that support detoxification, such as turmeric and bitter herbs. Latest research Title:“Folliculitis