Over view of the Urinary System: Embryology , Functions and Congenital Diseases
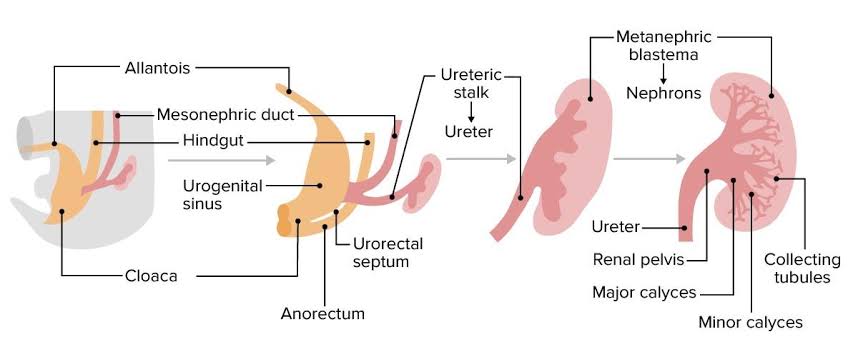
Introduction As we all know that nutrition is very essential to human body for its maintenance. Same as that body has to wash out all the waste and toxic substances which are produced after all the metabolic process , this work is done by excretory system also called as urinary system. COMPONENTS OF URINARY SYSTEM Development and Embryology of Urinary System This urinary system starts developing at 3rd week of Intrauterine life. This urinary system develops from the mesodermal ridge[Intermediate mesoderm] Bilaminar Disc Formation: The bilaminar disc forms during the 2nd week of embryonic development, following the process of implantation of the blastocyst into the uterine wall. Trilaminar Disc Formation: The trilaminar disc forms by the end of the 3rd week of development, during the process of gastrulation. Gastrulation is a crucial event that reorganizes the bilaminar disc into a three-layered structure, which will eventually give rise to all the organs and tissues of the body. Three divisions of Mesoderm: The Urinary System is mainly formed from the Intermediate Mesoderm. Formation of urinary system starts at week – 4 In 4th week of intra uterine life the intermediate mesoderm starts condensation and formation of nephrogenic cord and urogenital ridge takes place . Three overlapping kidney systems are formed from cranial to caudal region during the intra uterine life, they are : PRONEPHROS : These structures formed at the beginning of 4th week and these are rudimentary and non-functional occur in cervical region. These structures represented by 7 to 10 solid cell groups. These structures form vestigial excretory units called nephrotomes By the end of 4th week all indications of pronephric system have disappeared . MESONEPHROS : These structures are functional but for a short time , occurs in thoraco-lumbar region [upper L3 segments]. These mesonephros form mesonephric duct also called as wolffian duct and structures arise from this duct are called as mesonephric tubules. These mesonephros acts as primitive urinary system. Mesonephric duct which formed gets extended into cloaca and the mesonephric tubules form connections with the aorta through angiogenesis.[The process of formation of new blood vessels from existing blood vessel in body] NOTE : From the aorta the waste gets collected into the mesonephric tubules and from there through mesonephric duct they passed into cloaca .Cloaca is the structure which collects both urine and feces and send them to allantois , this is the structure which get modified into the anus and urinary bladder and urethra in later stage. These mesonephros works as primitive urinary system from week 5 to week 10 of intra uterine life . METANEPHROS : These structures are functional and permanent and forms kidney , these appear at 5th week. These metanephros are formed in pelvic region. The metanephros starts secreting growth factors which acts on mesonephric duct [wolffian duct] and induce formation of ureteric bud. Several important growth factors are involved in the interaction between the metanephros and ureteric bud: RECIPROCAL INDUCTION The ureteric bud (UB) plays a critical role in kidney development through a process called reciprocal induction, where it interacts with the surrounding metanephric mesenchyme to drive the formation of the functional structures of the kidney. Reciprocal induction refers to the mutual signaling between two different tissues to promote the development of one another. In the case of kidney development, the ureteric bud and metanephric mesenchyme interact in such a way that each tissue influences the development of the other. Reciprocal induction that works between the ureteric bud and the metanephric mesenchyme: 1. Ureteric Bud Signals to the Metanephric Mesenchyme The ureteric bud, once it outgrows from the mesonephric duct (Wolffian duct), interacts with the metanephric mesenchyme and induces it to undergo a process called mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET). This is essential for the formation of nephrons . 2. Metanephric Mesenchyme Signals to the Ureteric Bud In response to signals from the ureteric bud, the metanephric mesenchyme also sends signals back to the ureteric bud to control its growth and branching pattern. This reciprocal signaling is essential for the proper formation of both the nephron and the collecting system. Formation Of Renal Pelvis And Other Structures The uretic bud which extends into the metanephric blastomere through ureteric stalk forms renal pelvis . Renal pelvis form extensions and formation of major calyces takes place , these major calyces gives rise to minor calyces .At the ends of minor calyces origin of collecting tubules takes place[ approximately 1 to 3 million tubules]. The collecting tubules which are formed release growth factors and helps in condensation of metanephric blastomere at the place where it surrounds the collecting tubule to form metanephric mesodermal cap. This metanephric mesodermal cap get modified into metanephric vesicle and then into metanephric tubule and get fused with the collecting tubule to form distal convoluted tubule [DCT] , it goes on modifying and form proximal convoluted tubule [PCT] and bowman’s capsule respectively. The abdominal aorta divides into two branches at the pelvic region into right and left iliac arteries these form tuft of blood capillaries which form glomerular capillaries into bowman’s capsule of the nephron. During this stage the metanephric mesoderm deepens between the PCT and DCT which form loop of Henle. Hence , kidney develops from 2 sources : Position of kidney Initially it is situated in pelvic region later it shifts to more cranial position in the abdomen . In pelvic region the metanephros receive blood supply from the pelvic branch of aorta which gradually gets degenerated . During ascent to abdominal level, it is vascularized by arteries that originated from the aorta at continuously higher levels .The lower vessels gradually get degenerated ,at last kidneys are supplied by renal arteries which are developed lateral branches of aorta. Functions of Kidney The metanephros completely becomes functional at week 12 and take over all functions of kidney and mesonephric duct no longer plays any role in formation of urine it takes crucial role in formation of genital tract. Urine passed into the amniotic cavity and get mixes with the amniotic fluid