Table of Contents
- Introduction :
- Gait:
- Normal Gait :
- Important support phases :
- The Phases of Human Walking: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- GAIT ABNORMALITIES :
- Conclusion :
- References :
- Other articles :
Introduction :
Gait:
It is a medical term used for the way a person walks . In some people gait is abnormal may be due to some injury or due to under lying medical conditions.
Abnormal gait is also called as AMBULATORY DYSFUNCTION.
Any thing that affects brain, spinal cord, legs or feet leads to change in gait .
Normal Gait :
Normal gait is nothing but normal walking without any abnormalities . One complete gait cycle is completed when it begin with heel strike of a foot continues till heel strike of identical foot.
Human gait : It can be defined as a series of alternating movements of the lower extremities in a rhythmic motion that results in forward progression of body with minimal energy expenditure .
It means it takes 2 steps to complete a full gait cycle.
Gait cycle has 2 phases :
- Stance phase
- Swing phase
STANCE PHASE : The time duration of foot on ground , it occupies 60% of gait cycle . It starts when foot touches the ground and ends when the foot leaves the ground.
SWING PHASE : The time duration of foot in air, it occupies 40% of gait cycle .I t start when foot leaves the ground and end when same foot touches the ground again.
Important support phases :
SINGLE SUPPORT PHASE [Swing Phase] : In this phase only one limb is in contact with ground .
INITIAL DOUBLE SUPPORT PHASE : It is the sub phase between the heel contact to contralateral foot off. It shows 14 to 20% of stance phase .
TERMINAL DOUBLE SUPPORT PHASE : Itis sub phase from contralateral foot on to toe off, It shows 14 to 20% of stance phase .
TOTAL DOUBLE SUPPORT PHASE : It shows 28 to 40% of stance phase . As it is the sum of initial double support phase and terminal double support phase .
NOTE : More problems will appear during stance phase of gait when foot is loaded which in turn shows impact on the swing phase .
The Phases of Human Walking: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- STANCE PHASE:
- HEEL STRIKE [Contact Phase] : It is the point when initial contact with the ground is seen. It starts with lead leg first heel contact and ends with contralateral leg toe off. Usually it is considered around 14 to 20% of stance phase .
- LOADING RESPONSE[Foot Flat] : Initial double support during stance period .It takes around 16 to 22% of stance phase, starts with first heel contact of lead leg to first first contact of first metatarsal head of lead leg .
- MID STANCE : Time once other leg withdraws from the ground till weight is back on foot , it takes around 29 to 37% . It starts with toe off point of contralateral leg to the first point the heel comes off the ground of the lead leg .
- TERMINAL STANCE[Propulsive phase]: It is the time , once foot leaves the bottom marks top of stance phase and onset of swing part . It takes around 45-55% of stance phase .
- In this propulsive phase there are 2 phases one is ACTIVE and other is PASSIVE .
- ACTIVE PHASE : It is single support and considered around 31-35% . Stars at heel of point from the lead leg to first contact point for the contralateral leg .
- PASSIVE PHASE : It is double support phase and considered around 14-20%. Starts at heel contact of contralateral to toe off of the lead leg.
- In this propulsive phase there are 2 phases one is ACTIVE and other is PASSIVE .
- SWING PHASE:
- PRE-SWING PHASE : In this phase foot is pushed and raised off the bottom .
- TOE OFF : Instant when end or terminal contact is formed with the front of the feet .
- MID SWING : Instant when swinging foot exceeds the stance phase foot and each square measure together .
- TERMINAL SWING : Last extension of shank occurs the leg is aligned for starting foot contact to start out the new cycle .

GAIT ABNORMALITIES :
- ANTALGIC GAIT
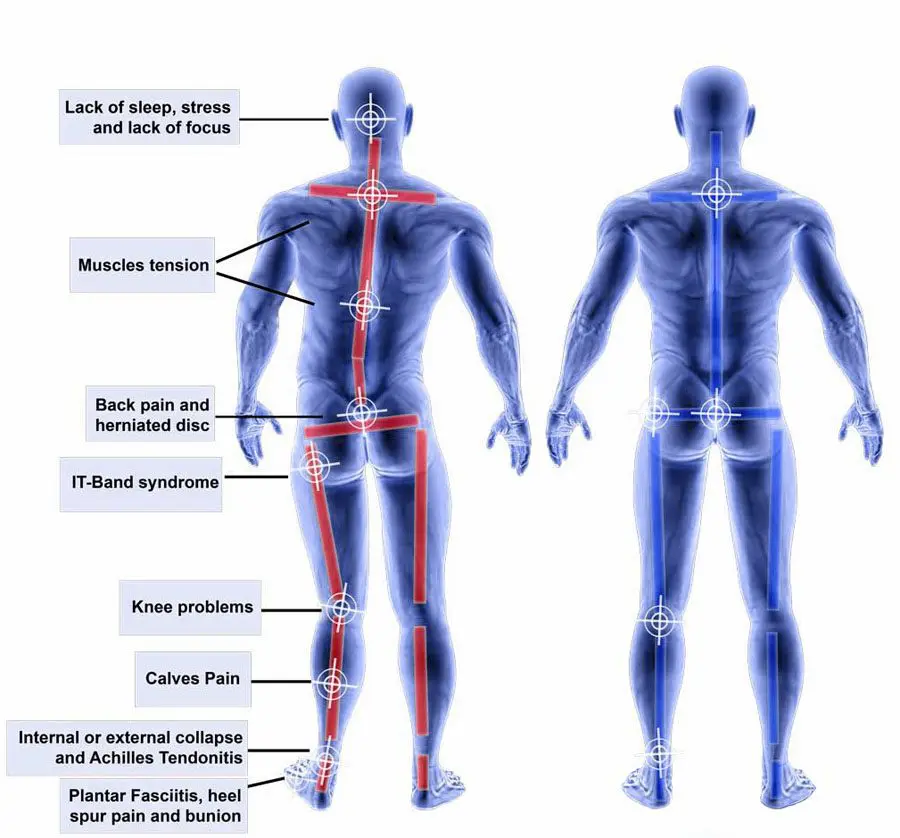
Most common type , resulted due to pain in lower extremities like pain in muscle , joints or in bones . Limping is seen this type of gait , means avoiding steeping or pressure on affected leg . keeping ankle fixed in the one position while lifting and lowering the foot. This may include following causes like :
- Arthritis
- Tendon or ligament injuries
- Muscle strains
- Low back issues, like sciatica
- Fractures
- Foot problems, like bunions or neuromas
- Infections
- Blood clots
- Bone malalignment after healing from a fracture
- Rickets
2.PROPULSIVE GAIT :
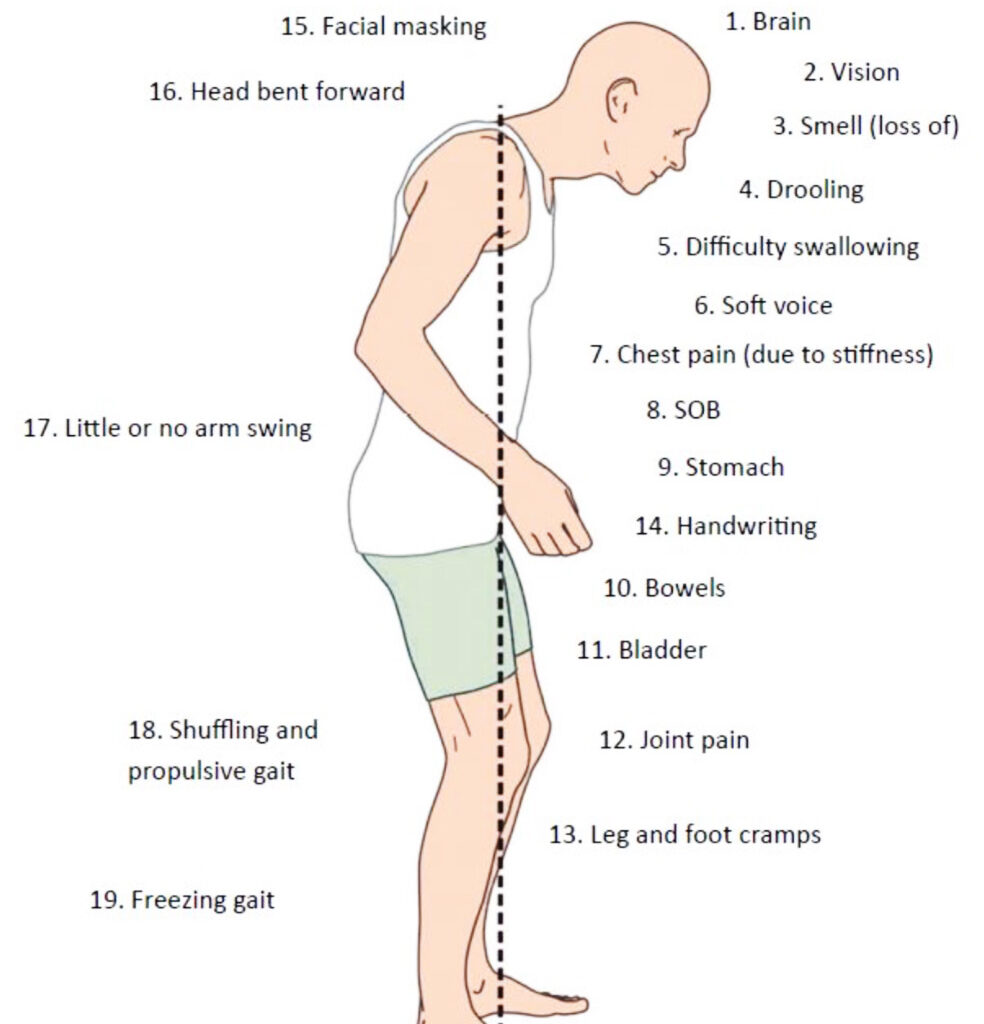
It is also called as PARKINSONS GAIT or FESTINATING GAIT . As it is seen in Parkinson’s disease , one can observe stooping means head and neck are bend forwards and downward and rigid posture is seen . Steps are short and fast to maintain center of gravity, hence called as festinating gait .Also seen in carbon monoxide poison .
3 .SCISSORS GAIT :
In this type the knees and thighs hits or cross in a scissor like pattern during walk and slow and small steps are seen and this type of gait is diagnosed in spastic cerebral palsy. severe adduction of legs and hitting of the knees and thighs .

4. SPASTIC GAIT :
It is also called as hemiplegic gait ,In this type of gait one leg is stiffened while walking . If lifted to walk it is either dragged or swings around in semicircular motion [ circumduction ] . This condition is seen in cerebral palsy , multiple sclerosis , Hemiplegia.

5. STEPPAGE GAIT :
It is also called as neuropathic gait ,in this high step is seen means person elevates hip to lift leg higher than normal . Foot appears floppy when it drops and toes point down and scrape ground this type of gait is diagnosed in muscle atrophy or peroneal nerve injury [ like in spinal stenosis or herniated disc ]

6.WADDILING GAIT :
In this exaggerate movement of upper body is observed like a duck , hence it is also called as duck walk . This type of gait is diagnosed in hip dislocation , progressive muscular dystrophy. It is also called as myopathic gait . Some times pregnancy women also adopt waddling gait as protective measure to prevent falling.

7. CROUNCHING GAIT :
In this gait flexing of ankles, knees and hip is seen while walking . Characteristics like bending down while walking , toe dragging are seen this gait abnormality is diagnosed in cerebral palsy.

8. ATAXIC GAIT :
In this irregular steps , person can’t walk in straight line when walk heel to toe [ unsteady walk ]. This abnormality is diagnosed in cerebellar degeneration .Vitamin deficiencies like low levels of vitamin E, B-1, or B-12 and in Sensory disturbances like vision or proprioception disorders

9. SHUFFLING GAIT :
In this type of gait feet is not completely lifted off the ground and feet get dragged while walking . This type of gait is seen in medical conditions like Parkinson’s disease , Muscle strain and in nerve damage conditions etc. Symptoms like shot steps ,stooped posture , flexed knees are observed .

10. LURCHING GAIT :
This type of gait abnormality is caused due to paralysis or weakness of gluteus muscles or other conditions that affect the hip or legs . In this gait type one may observe slow and long stride .

Conclusion :
In conclusion, understanding the various types of gait is essential for recognizing and addressing different physical conditions and movement patterns. Gait analysis plays a crucial role in diagnosing and treating mobility issues, whether they stem from neurological disorders, orthopedic injuries, or natural aging. By studying common gait types such as the antalgic, ataxic, and spastic gaits, medical professionals can develop targeted interventions and rehabilitation plans. Additionally, the influence of environmental factors and individual differences in biomechanics further emphasizes the need for personalized care. Overall, analyzing and categorizing gait types not only aids in better medical outcomes but also promotes the importance of early detection and proactive management in maintaining overall mobility and quality of life.
References :
A_Review_on_Clinical_Gait_Analysis
Other articles :
- Global Perspectives on Folliculitis: Ayurveda’s Approach to Prevention, Treatment, and Healthcare Disparities
- How to Lose Weight in 1 Week: Ayurvedic and Research-Based Insights
- 50 Research Paper Insights into Sleep: The Ultimate Guide to Health, Cognitive Performance, and Longevity
- Top 20 Most comely Useful Instruments in Physiology lab with their classification- part 4
- BEST AYURVEDIC DIET AND NUTRITION GUIDE
- AYURVEDA INTRODUCTION
- Growth of the Ayurveda Wellness Market in 2024: Personalization, Technology, and Global Expansion
- Shat Kriyakala: Understanding 6 Stage of Disease Progression in Ayurveda and Its Modern Relevance
- Understanding Concepts 3 Doshas in Ayurveda: Tridosha
- Anatomy, Function, and Clinical Insights into the Mediastinum: A Comprehensive Overview
- Stress Relief and Mental Wellness: Understanding Causes, Effects and Effective Strategies
- Arthritis explore Ayurvedic and Modern Aspects
- Over view of the Urinary System: Embryology , Functions and Congenital Diseases






Pingback: India’s Ancient Science, Global Validation: Time to Embrace Our Heritage -