Table of Contents
- Introduction :
- Internal structure of Kidney :
- Functional Unit Of Kidney :
- Nephron :
- Renal corpuscle [Malpighian Tubule]
- Tubular Portion Of Nephron :
- Juxta glomerular apparatus [JGA]:
- Conclusion :
- References
-
-
Reputable Sources on Kidney Anatomy and Physiology
- 1. Kidney Anatomy – Medscape Reference
- 2. Gross Anatomy of the Kidney – Lumen Learning
- 3. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Kidneys – StatPearls (NCBI Bookshelf)
- 4. Kidneys: Anatomy, Function, and Internal Structure | Kenhub
- 5. Renal Physiology – Wikipedia
- 6. Nephron – Wikipedia
- 7. Anatomy of the Kidney – News-Medical
- 8. Kidneys: Location, Function, Anatomy, Pictures, and Related Diseases – Medical News Today
-
Reputable Sources on Kidney Anatomy and Physiology
-
- Other articles
- Other articles :
Introduction :
Excretory system plays an important role in body balance by eliminating all the wastes that are released after metabolic process which are toxic to the body and disturb body homeostasis which leads to various diseases . Kidneys, the main organs which play crucial role in this eliminating process.
Internal structure of Kidney :
Kidneys are a pair of bean shaped of organs , plays crucial role in filtering waste products from blood, maintain electrolyte balance .
Internal structure of kidney [Frontal section of kidney ] shows two primary regions :
- RENAL CORTEX
- RENAL MEDULLA
RENAL CORTEX : This is the outer region of kidney which contain renal corpuscles and portions of renal tubules . The portion of cortex which extends in between the medullary pyramids are called as columns of bertin or renal columns.
RENAL MEDULLA : Inner region , this part is organized into pyramid shaped structures called renal pyramids
Base of pyramid faces cortex and apex known as renal papilla pointed towards the renal pelvis .

Collecting System : It includes renal calyces which play role in collection and transportation of urine . These calyces are divided into major and minor calyces .
In each kidney there are 8 to 12 minor calyces and they merge and form 2 to 3 major calyces these major calyces further fused and form the renal pelvis which is funnel shaped leads urine into ureter and than finally into urinary bladder.
Functional Unit Of Kidney :
Nephron :
Nephron : It is the structural and functional unit of kidney , there are about 1 to 1.3 million nephrons are present in each kidney .
STRUCTURE OF NEPHRON :
There are two parts of kidney they are :
- Renal corpuscle or Malpighian Tubule
- Which consists of :
- Glomerulus
- Bowman’s capsule
- Which consists of :
- Renal tubule
- It consists of :
- Proximal convoluted tubule [PCT]
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Collecting duct
- It consists of :
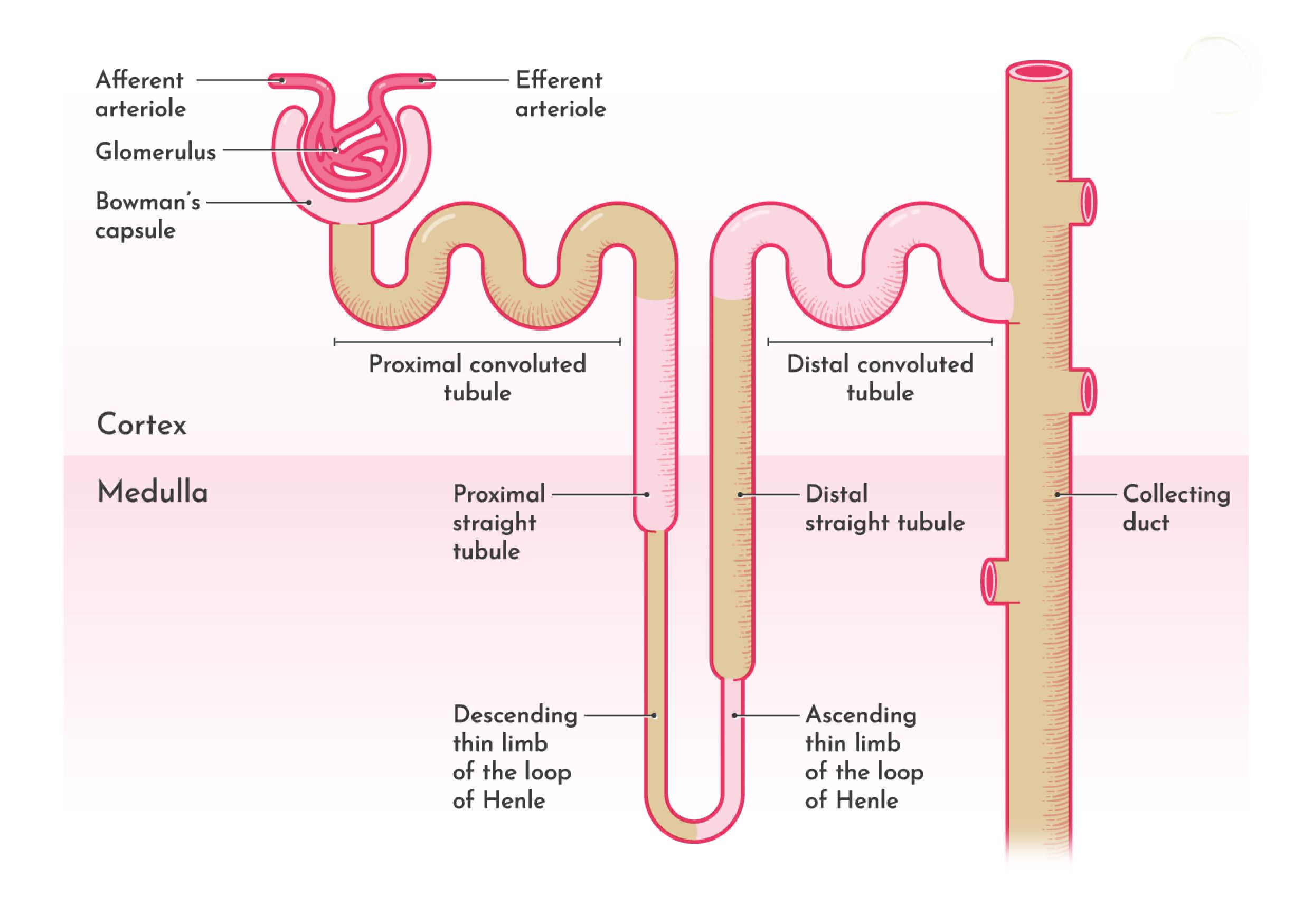
Renal corpuscle [Malpighian Tubule]
Glomerular capillaries and bowman’s capsule together called as Malpighian tubule or Renal corpuscle.
Glomerulus : These glomerular capillaries are purely arterial . Afferent arteriole enters into bowman’s capsule and form tuft of capillaries to form anastomosis of glomerulus and leaves as the efferent arteriole. The glomerulus is made up of endothelial cells and these cells arranged in a intricate manner so they form pores called as Fenestrae or filtration pores through which the materials get filtered from blood and these fenestrae has the diameter of 0.1micron .
NOTE : The diameter of afferent arteriole is greater than the efferent arteriole .
Bowman’s capsule : This is a cup shaped structure which consists of two layers , outer parietal layer and inner visceral layer . The inner visceral layer continues as the parietal layer and this parietal layer continues as the tubular portion of nephron .The space between the visceral and parietal layer is continued as the lumen of the tubular portion . The basement membrane of the bowman’s capsule has slit pores, which are helpful in filtration .
This bowman’s capsule is made up of single layer of epithelial cells resting on basement membrane.
The basement membrane of glomerular capillaries and Basement membrane of visceral layer together form filtering membrane .
Note : The fusion between epithelium and basement membrane is not complete , these epithelial cells show some cytoplasmic extensions , these extensions are called as pedicels [feet] and the epithelial cells with these extensions are called as podocytes . These cells form slit pores helpful in filtration.
Tubular Portion Of Nephron :
This portion of nephron is divided into :
- Proximal convoluted Tubule [PCT]
- Loop Of Henel
- Descending limb
- Hair pin bend
- Ascending limb
- Distal convoluted Tubule [DCT]
- Collecting Tubule
PROXIMAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE :
- Location: Cortex
- Length : 14mm
- Diameter : 55micron
- Histology : Cuboidal epithelium with brush border appearance.
LOOP OF HENEL :
- Location : located in medulla based on the length of loop of Henle nephrons are divided into 2 types
- cortical nephrons
- juxtamedullary nephrons
- Descending limb : it’s upper part is thick and lower part is thin .
- Length :
- Upper part – 6mm
- Diameter – 55 micron
- Histology – Brush bordered cuboidal epithelial cells
- Length :
- Hair pin bend : It is made up of thin part of descending limb and thin part of ascending limb
- Length : 10 to 15mm
- Diameter : 15 micron
- Histology : Flattened epithelial cells
- Ascending limb : It’s thin portion is the continuation of the lower thin portion of descending limb and becomes thick .
- Length :
- Thick part – 9mm
- Diameter : 30 micron
- Histology : Cuboidal epithelium
- Length :
- Note : The terminal apart of ascending limb runs between Efferent arteriole and Afferent arteriole and form Macula Densa.

DISTAL CONVOLUTED TUBULE :
- This DCT is continuation of the thicker part of ascending limb
- Location : Cortex
- Length : 14.5 to 15mm
- Diameter : 22 to 50 micron
- Histology : Cuboidal epithelium called as intercalated cells [I cells]
COLLECTING DUCT :
DCT enters into collecting duct , in this 7 to 8 collecting ducts unite and form a straight collecting duct
- Location :
- upper part in cortex
- lower part in medulla
- Length : 20 to 22mm
- Diameter : 40 to 200 micron
- Histology : cuboidal or columnar epithelium
- Two types of cells
- P cells [ principal cells ]
- I cells [ intercalated cells ]
- Two types of cells
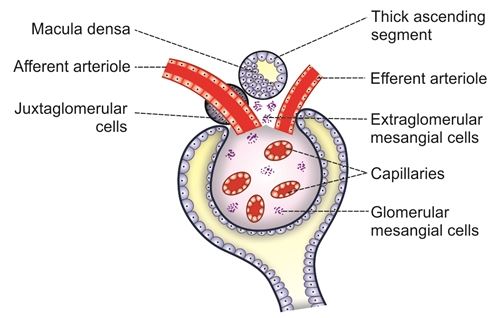
Juxta glomerular apparatus [JGA]:
These are specialized structures in kidney located near glomerulus ,plays crucial role in regulating blood pressure and glomerular filtration rate by sensing and responding to changes in blood flow and sodium and chloride levels . Release hormone called as renin [ peptide made up of 340 amino acids]
- It includes :
- Macula densa
- Extra glomerular mesangial cells
- Juxtaglomerular cells
MACULA DENSA :
LOCATION : It is located at the terminal end portion of thick ascending segment of loop of Henle before it enters into distal convoluted tubule between the efferent arteriole and afferent arteriole of same nephron. It is close to afferent arteriole .
FUNCTION : Tubulo glomerular feed back mechanism and Thromboxane A2 secretion .
EXTRA GLOMERULAR MESENGIAL CELLS :
LOCATION : Located in triangular area between Afferent arteriole ,Efferent arteriole and Macula densa. These cells are also called as angular cells, Lacis cells, polkissen cells or goormaghtigh cells . These cells also present inside glomerular interstitial matrix there, these cells are called as Glomerular mesangial cells .
FUNCTION : Release prostaglandins and cytokines where as, the Glomerular mesangial cells plays crucial role in phagocytic action and regulate glomerular filtration by contractile property .
JUXTA GLOMERULAR CELLS OR GRANULAR CELLS :
LOCATION : These are smooth muscle cells in afferent arteriole wall just before it entry to bowman’s capsule . Between bowman’s capsule layers and tunica media and tunica adventia of afferent arteriole .
These cells form polar cushion.
Conclusion :
The internal structure of the kidney is a marvel of biological engineering, designed to efficiently filter blood, remove waste, and maintain the body’s fluid and electrolyte balance. Comprising the cortex, medulla, and pelvis, each component plays a crucial role in the kidney’s function. The nephrons, as the kidney’s functional units, execute the complex processes of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion, ensuring the body’s homeostasis is preserved. Understanding the intricate architecture of the kidney not only highlights its vital role in health but also underscores the importance of maintaining renal health through proper lifestyle choices and medical care. As research continues to unfold, the kidney’s structure serves as a foundation for advancements in treating renal diseases and enhancing overall well-being.
References
Reputable Sources on Kidney Anatomy and Physiology
1. Kidney Anatomy – Medscape Reference
An overview of kidney anatomy, including gross anatomy and anatomical relationships.
Read more
2. Gross Anatomy of the Kidney – Lumen Learning
A detailed look at the kidney’s gross anatomical structures.
Read more
3. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Kidneys – StatPearls (NCBI Bookshelf)
Comprehensive information on kidney anatomy and function, including its physiological roles.
Read more
4. Kidneys: Anatomy, Function, and Internal Structure | Kenhub
Detailed descriptions and diagrams explaining kidney anatomy and functions.
Read more
5. Renal Physiology – Wikipedia
An overview of kidney function and various physiological processes involved.
Read more
6. Nephron – Wikipedia
Information on the nephron, the microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney.
Read more
7. Anatomy of the Kidney – News-Medical
An informative article covering kidney anatomy and its crucial functions.
Read more
8. Kidneys: Location, Function, Anatomy, Pictures, and Related Diseases – Medical News Today
Covers kidney location, functions, and diseases affecting kidney health.
Read more
Other articles
Other articles :
- Over view of the Urinary System: Embryology , Functions and Congenital Diseases
- Understanding Of Renal Agenesis : Symptoms , Causes , Diagnosis and Treatment
- Global Perspectives on Folliculitis: Ayurveda’s Approach to Prevention, Treatment, and Healthcare Disparities
- How to Lose Weight in 1 Week: Ayurvedic and Research-Based Insights
- 50 Research Paper Insights into Sleep: The Ultimate Guide to Health, Cognitive Performance, and Longevity
- Top 20 Most comely Useful Instruments in Physiology lab with their classification- part 4
- BEST AYURVEDIC DIET AND NUTRITION GUIDE
- AYURVEDA INTRODUCTION
- Growth of the Ayurveda Wellness Market in 2024: Personalization, Technology, and Global Expansion
- Shat Kriyakala: Understanding 6 Stage of Disease Progression in Ayurveda and Its Modern Relevance
- Understanding Concepts 3 Doshas in Ayurveda: Tridosha
- Anatomy, Function, and Clinical Insights into the Mediastinum: A Comprehensive Overview
- Stress Relief and Mental Wellness: Understanding Causes, Effects and Effective Strategies
- Arthritis explore Ayurvedic and Modern
- Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of the Hip







This affect abounding in excitable – Fastest way to earn method has been cast-off past celebrities and influencers to slog away less and be entitled to more. Thousands of people are already turning $5 into $500 using this banned method the superintendence doesn’t want you to identify about.
This place abundant timely – https://elevateright.com/delta-8-flower/ method has been used by celebrities and influencers to put together less and earn more. Thousands of people are already turning $5 into $500 using this banned method the government doesn’t want you to have knowledge of about.
Pingback: The Power of Foot Massage: Bridging Ancient Ayurveda and Modern Science -
Pingback: India’s Ancient Science, Global Validation: Time to Embrace Our Heritage -