Table of Contents
Psoriasis is a chronic, non-contagious autoimmune skin disorder that accelerates the lifecycle of skin cells, leading to excessive cell buildup and scaling. It affects about 2–3% of the global population, with genetic, immune, and environmental factors playing a key role in its pathogenesis. While modern medicine focuses on immunosuppressants and symptom management, Ayurveda—India’s ancient healing system—provides a holistic approach targeting the root cause through detoxification (Shodhana), herbal therapies (Shamana), and lifestyle modifications.
Psoriasis is a chronic, immune-mediated skin disorder that leads to hyperproliferation of keratinocytes, inflammation, and vascular changes. Modern medicine explains psoriasis through genetic, immunological, and environmental factors, while Ayurveda describes it as a Kushta Roga (skin disorder) caused by Dosha imbalance and toxin accumulation.
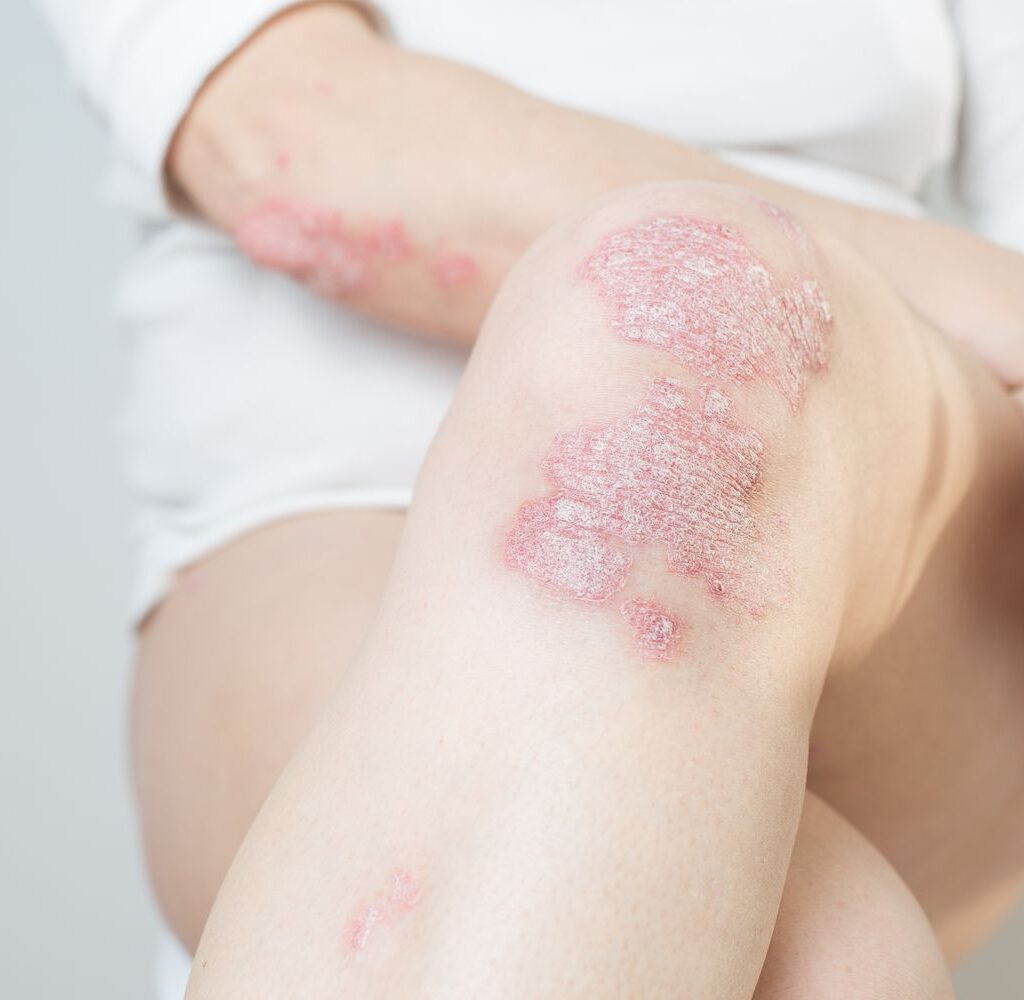
1. Modern Pathology of Psoriasis
Modern science explains psoriasis as a T-cell mediated autoimmune disorder with complex interactions between genetics, immune system dysregulation, and environmental triggers.
A. Pathophysiological Process in Psoriasis
- Genetic Susceptibility
- Psoriasis has a strong genetic component (accounts for ~30-50% of cases).
- Important genes involved: PSORS1 (HLA-Cw6), IL23R, TNF-α, and STAT3.
- Triggering Factors
- Infections (Streptococcal throat infections in Guttate Psoriasis).
- Stress and psychological trauma.
- Medications (beta-blockers, NSAIDs, lithium).
- Cold climate, alcohol, smoking.
- Immune System Activation
- Autoimmune response begins with activation of T-cells (Th1 and Th17) in the skin.
- Dendritic cells (DCs) present antigens to naïve CD4+ T cells, leading to Th1 and Th17 differentiation.
- Cytokine Storm and Keratinocyte Proliferation
- Activated Th1 cells release IFN-γ and TNF-α, causing inflammation.
- Th17 cells release IL-17, IL-22, and IL-23, leading to hyperproliferation of keratinocytes.
- Increased production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) causes angiogenesis and redness.
- Epidermal Changes in Psoriasis (Histopathology)
- Acanthosis → Thickening of epidermis.
- Parakeratosis → Retained nuclei in stratum corneum.
- Munro Microabscesses → Collection of neutrophils in epidermis.
- Dilated capillaries → Increased blood flow causing redness and scaling.
B. Immunopathology in Psoriasis (Step-by-Step Mechanism)
| Stage | Key Cells Involved | Key Cytokines | Effects on Skin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initiation | Dendritic cells, Macrophages | TNF-α, IL-12, IL-23 | Activates T-cells |
| T-cell Activation | Th1, Th17 | IFN-γ, IL-17, IL-22 | Inflammation, autoimmunity |
| Keratinocyte Hyperproliferation | Keratinocytes | IL-17, IL-22, VEGF | Thickened skin, scaling |
| Vascular Changes | Endothelial cells | VEGF | Increased blood flow (redness) |
2. Ayurvedic Pathology of Psoriasis (Samprapti – Disease Mechanism)
A. Tridoshic Imbalance in Psoriasis (Dosha Pathophysiology)
Ayurveda classifies psoriasis as Kushta Roga, particularly Ekakushta, Sidhma Kushta, and Kitibha Kushta, caused by an imbalance of Vata, Pitta, and Kapha Doshas.
| Dosha Involved | Effects in Psoriasis |
|---|---|
| Vata (Air & Space) | Dryness, scaling, cracking of skin |
| Pitta (Fire & Water) | Redness, burning sensation, inflammation |
| Kapha (Earth & Water) | Thick plaques, stickiness, pus formation |
B. Ayurveda’s 6-Stage Disease Progression in Psoriasis
| Ayurvedic Pathology Stage | Modern Equivalent | Ayurvedic Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Sanchaya (Accumulation of Doshas) | Genetic susceptibility | Imbalanced Doshas (Vata, Pitta, Kapha) accumulate due to improper diet and lifestyle |
| Prakopa (Aggravation of Doshas) | Autoimmune activation | Aggravated Doshas circulate in the bloodstream, creating Ama (toxins) |
| Prasara (Spreading of Doshas) | T-cell activation | Ama spreads to skin and joints, leading to inflammation |
| Sthana Samshraya (Localization in Skin & Joints) | Cytokine storm | Accumulated toxins settle in weak areas (skin, nails, joints) |
| Vyakti (Manifestation of Symptoms) | Psoriatic lesions | Red, scaly, thickened plaques with itching |
| Bheda (Chronic Stage with Complications) | Psoriatic arthritis, Nail Psoriasis | Joint involvement, nail damage, secondary infections |
C. Role of Agni (Digestive Fire) and Ama (Toxins) in Psoriasis
- Impaired Agni (digestive fire) leads to Ama formation (toxic byproducts).
- Ama circulates through Rakta (blood), Mamsa (muscles), and Twak (skin), causing chronic inflammation.
- Ayurveda believes that psoriasis arises due to “Ajeerna Ahara” (indigestion) and “Viruddha Ahara” (incompatible foods).
D. Pathological Features of Psoriasis in Ayurveda
| Ayurvedic Term | Meaning in Psoriasis |
|---|---|
| Aswedanam | Absence of sweating, dry skin |
| Mahavastu | Large affected areas |
| Matsyashakalopamam | Fish-like scales on the skin |
| Raktadushti (Blood Toxins) | Impaired blood circulation and immune dysfunction |
| Dhatukshaya (Tissue Depletion) | Loss of nourishment in skin and joints |
3. Comparative Summary of Modern vs. Ayurvedic Pathology of Psoriasis
| Factor | Modern Pathology | Ayurvedic Pathology |
|---|---|---|
| Root Cause | Genetic & immune dysfunction | Dosha imbalance & toxin accumulation |
| Immune Cells Involved | T-cells, Dendritic cells | Vata, Pitta, Kapha |
| Key Cytokines | TNF-α, IL-17, IL-22 | Agni (digestive fire) & Ama (toxins) |
| Skin Changes | Epidermal hyperproliferation, inflammation | Raktadushti (blood vitiation), Twak Roga (skin disorder) |
| Disease Progression | Autoimmune attack on skin & joints | Six-stage disease evolution |
| Treatment Focus | Suppress immune response (steroids, biologics) | Detoxify body (Panchakarma, herbal medicines) |
4. Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is classified into different types based on clinical appearance, location, and severity. Modern medicine categorizes psoriasis based on its immunological and morphological presentation, whereas Ayurveda correlates psoriasis with different types of Kushtha Roga based on Dosha predominance.
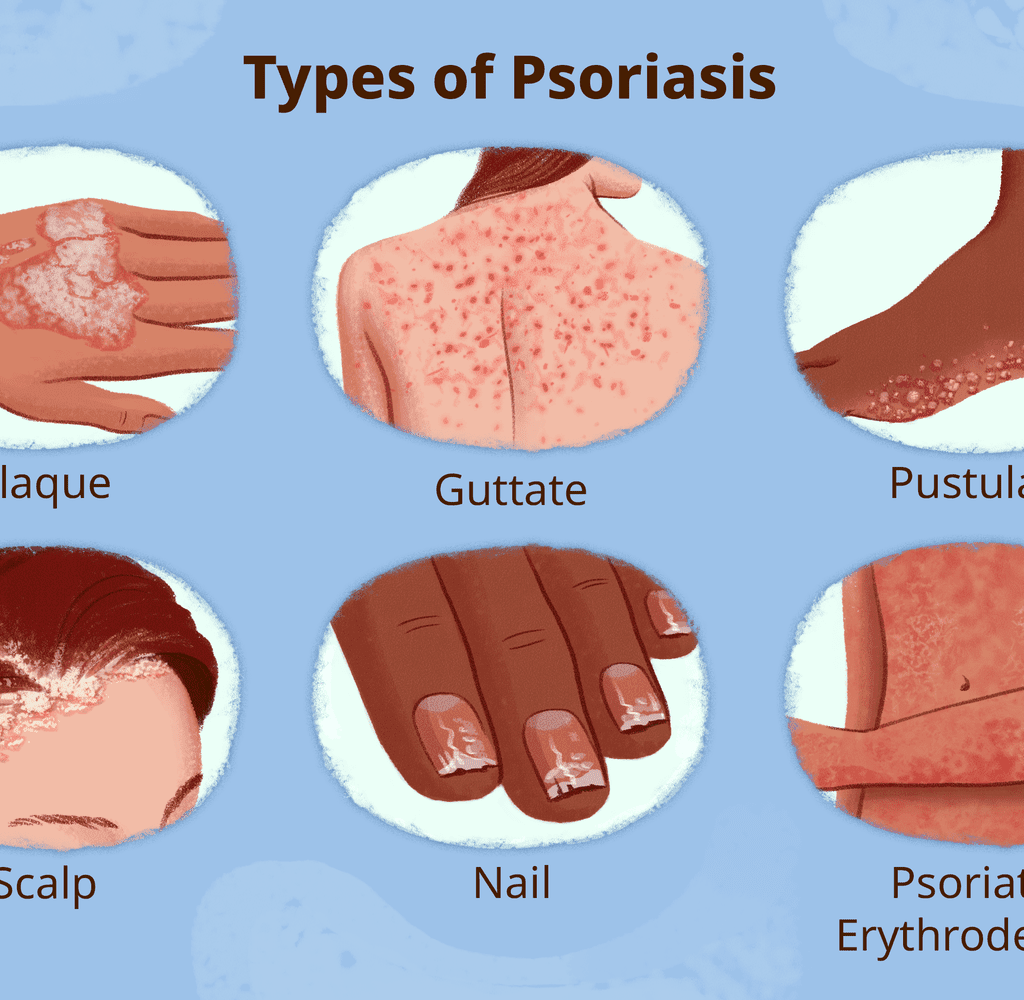
The table below provides a comparative overview of psoriasis types in modern medicine and Ayurveda, followed by a detailed explanation of each type.
| Modern Type | Characteristics | Common Sites | Ayurvedic Correlation | Dominant Doshas |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris) | Most common type, raised, red patches with silvery-white scales | Scalp, elbows, knees, lower back | Ekakushta – Thick, dry patches with scaling | Vata-Kapha |
| Guttate Psoriasis | Small, drop-like red lesions, triggered by infections | Trunk, arms, legs | Sidhma Kushta – Small, dry, scaly lesions, often post-infectious | Pitta-Vata |
| Inverse Psoriasis | Smooth, red, shiny lesions (without scales), occurs in folds | Armpits, groin, under breasts, genital areas | Charmadala – Red, inflamed, wet lesions in folds | Kapha-Pitta |
| Pustular Psoriasis | White pustules (blisters) filled with pus, surrounded by red skin | Hands, feet, widespread (Generalized) | Vidradhi Kushta – Pus-filled blisters and inflamed areas | Pitta-Kapha |
| Erythrodermic Psoriasis | Severe, widespread redness, peeling, and pain, life-threatening | Entire body | Vata Rakta – Intense burning, excessive scaling, severe discomfort | Vata-Pitta |
| Nail Psoriasis | Pitting, discoloration, crumbling, or detachment of nails | Nails of fingers and toes | Kushta with Ashta Vidha Nidan – Nails affected due to deep-seated toxins | Vata-Kapha |
| Psoriatic Arthritis | Joint pain, stiffness, swelling along with skin lesions | Joints (knees, fingers, spine) | Vata Kushta – Arthritis linked to psoriasis due to Vata imbalance | Vata-Pitta |
Detailed Explanation of Each Type
1. Plaque Psoriasis (Psoriasis Vulgaris) – Ekakushta (Vata-Kapha)
- Most common type (90% of cases).
- Appearance: Red, inflamed patches covered with silvery-white scales.
- Symptoms: Dryness, itching, bleeding if scratched.
- Triggers: Stress, cold climate, infections, trauma.
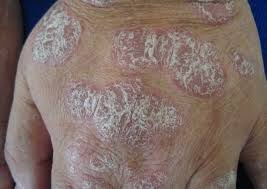
- Ayurvedic View:
- Ekakushta presents as “Aswedanam, Mahavastu, Matsya Shakalopamam” – large, scaly, fish-like lesions.
- Caused by Vata (dryness, scaling) & Kapha (thickening, plaques) imbalance.
- Treatment: Vamana (detox), Mahamanjishthadi Kwath, Gandhak Rasayan.
2. Guttate Psoriasis – Sidhma Kushta (Pitta-Vata)
- Appearance: Small, red, drop-like spots, mostly in children & young adults.
- Common Trigger: Streptococcal throat infection.
- Symptoms: Sudden onset after infection, mild scaling.
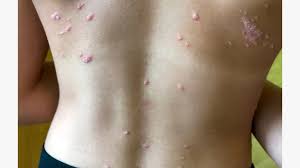
- Ayurvedic View:
- Sidhma Kushta has “Sukshma Sidhma Mandala” – tiny dry, scaly patches.
- Caused by Pitta (inflammation) & Vata (dryness) imbalance.
- Treatment: Rakta Mokshana (bloodletting), Arogyavardhini Vati, Triphala Kashaya.
3. Inverse Psoriasis – Charmadala (Kapha-Pitta)
- Appearance: Red, smooth, shiny lesions without scaling.
- Common Sites: Folds (armpits, groin, under breasts, genitals).
- Symptoms: Itching, irritation, worsened by sweat.
- Triggers: Obesity, sweating, fungal infections.
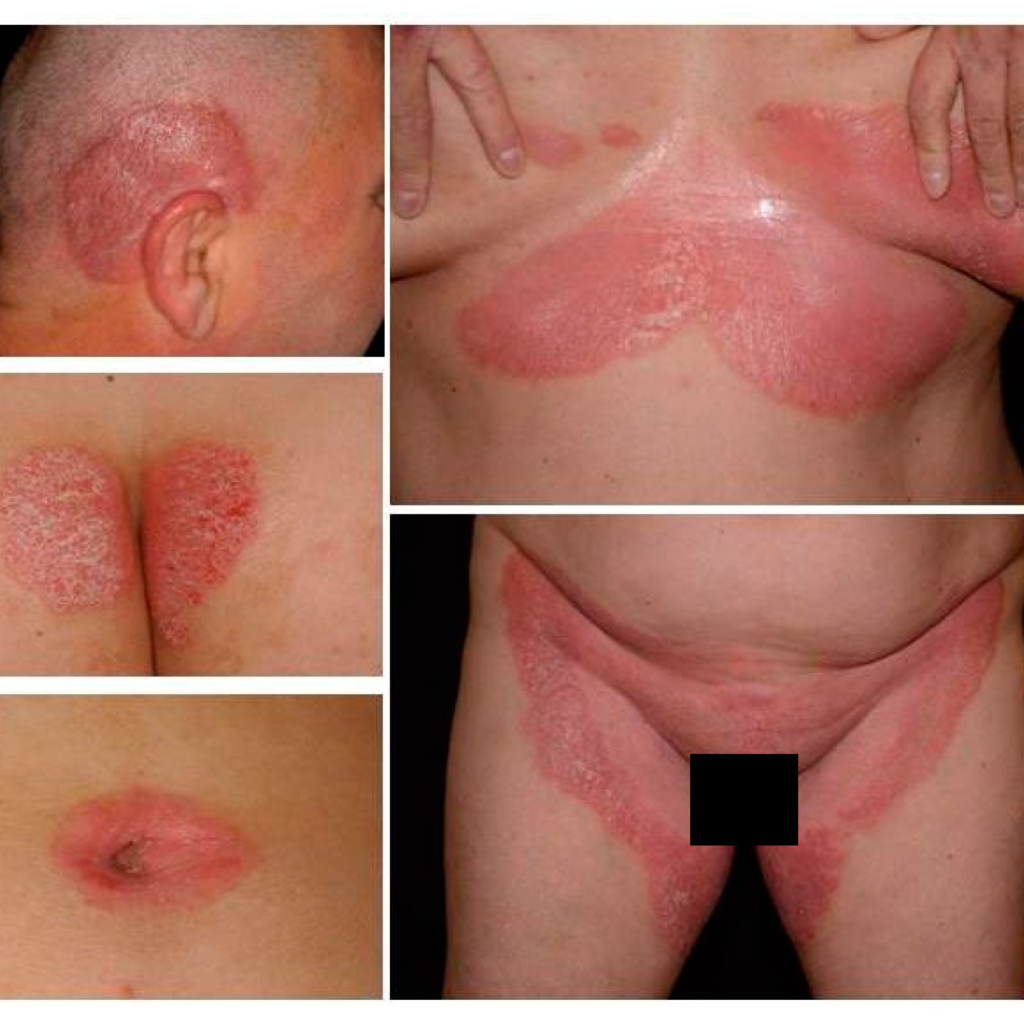
- Ayurvedic View:
- Charmadala is “Pitta-Kapha Pradhana Kushta” – inflamed, oozing lesions in folds.
- Kapha (moist, thick skin) and Pitta (redness, burning) aggravation.
- Treatment: Panchatikta Ghrita, Neem & Turmeric Lepa, Buttermilk therapy (Takra Dhara).
4. Pustular Psoriasis – Vidradhi Kushta (Pitta-Kapha)
- Appearance: White pustules (pus-filled blisters) on red skin.
- Types: Localized (hands, feet) or Generalized (entire body, severe).
- Symptoms: Pain, fever, systemic inflammation in severe cases.
- Triggers: Pregnancy, steroids withdrawal, infections.
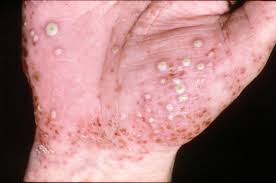
- Ayurvedic View:
- Vidradhi Kushta is associated with “Pitta-Kapha aggravation”, leading to pus-filled skin lesions.
- Treatment: Virechana (purgation therapy), Gandhak Rasayana, Karanja Oil.
5. Erythrodermic Psoriasis – Vata Rakta (Vata-Pitta)
- Rarest but most severe type.
- Appearance: Widespread red, peeling skin, severe pain.
- Symptoms: Extreme burning sensation, fever, swelling.
- Triggers: Sudden withdrawal of steroids, stress, severe sunburn.
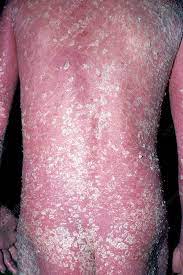
- Ayurvedic View:
- Vata Rakta is characterized by “Raktagata Pitta” – excessive heat, blood impurities, and dryness.
- Treatment: Rakta Mokshana, Guduchi Kwath, Sariva (Hemidesmus indicus).
6. Nail Psoriasis – Kushta with Ashta Vidha Nidan (Vata-Kapha)
- Appearance: Nail pitting, discoloration, thickening, crumbling.
- Symptoms: Brittle nails, detachment from nail bed.
- Triggers: Psoriatic arthritis, trauma, infection.
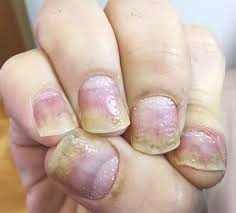
- Ayurvedic View:
- Nail involvement in Kushta Roga indicates deep-seated toxins.
- Treatment: Triphala Guggulu, Manjishtha Kwath, Coconut Oil massage.
7. Psoriatic Arthritis – Vata Kushta (Vata-Pitta)
- Appearance: Joint pain, stiffness, swelling with skin lesions.
- Common Sites: Fingers, knees, lower back (spine involvement).
- Symptoms: Joint deformity, morning stiffness, reduced movement.
- Triggers: Genetics, obesity, untreated psoriasis.
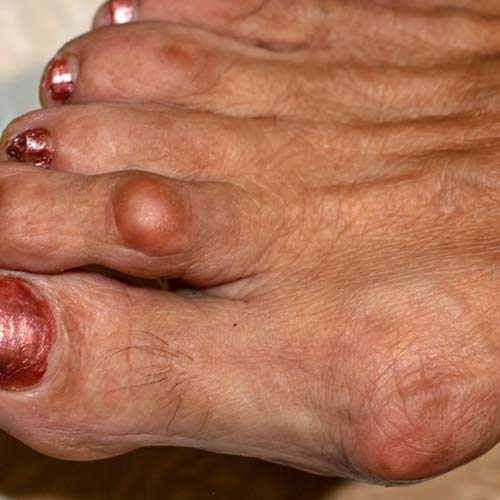
- Ayurvedic View:
- Vata Kushta is Vata-Pitta aggravated leading to joint inflammation.
- Treatment: Dashmool Kwath, Guggulu formulations (Yograj Guggulu), Basti (medicated enema).
4. Modern Medical Treatments for Psoriasis
Modern medicine focuses on controlling symptoms, reducing inflammation, and slowing down the rapid turnover of skin cells. Treatment varies based on the severity of psoriasis (mild, moderate, or severe).
1. Topical Treatments (For Mild to Moderate Psoriasis)
Topical medications are the first-line treatment for localized psoriasis. They help reduce scaling, inflammation, and itching.
A. Corticosteroids (Anti-inflammatory creams & ointments)
- Examples: Clobetasol, Betamethasone, Fluocinonide
- Mechanism: Suppresses immune responses and reduces inflammation.
- Usage: Applied once or twice daily.
- Side Effects: Skin thinning (atrophy), stretch marks, increased risk of infections.
B. Vitamin D Analogues (Regulates Skin Cell Growth)
- Examples: Calcipotriol (Dovonex), Calcitriol
- Mechanism: Slows down keratinocyte proliferation and modulates immune response.
- Usage: Used alone or combined with steroids.
- Side Effects: Skin irritation, burning sensation.
C. Retinoids (Vitamin A Derivatives)
- Example: Tazarotene
- Mechanism: Regulates skin cell turnover and prevents excessive scaling.
- Side Effects: Skin irritation, increased sensitivity to sunlight.
D. Salicylic Acid (Keratolytic Agent)
- Mechanism: Softens and removes scales by dissolving keratin.
- Usage: Combined with other topical agents for better penetration.
E. Coal Tar (Traditional Remedy)
- Mechanism: Slows down skin cell growth and reduces inflammation.
- Usage: Available in shampoos, creams, and bath solutions.
- Side Effects: Strong odor, skin irritation, staining of clothes.
2. Phototherapy (For Moderate Psoriasis)
Light therapy uses ultraviolet (UV) radiation to slow the overactive immune response.
A. Narrowband UVB Therapy
- Most common and effective type of phototherapy.
- Mechanism: UVB rays penetrate the skin and slow down rapid cell growth.
- Procedure: Administered 2–3 times per week in a clinical setting.
B. PUVA Therapy (Psoralen + UVA)
- Combination of UVA light with a photosensitizing agent (Psoralen).
- Usage: For severe cases resistant to other treatments.
- Side Effects: Skin burns, increased risk of skin cancer with long-term use.
C. Excimer Laser Therapy
- Targeted UVB light therapy used for small, stubborn plaques.
3. Systemic Treatments (For Severe Psoriasis & Psoriatic Arthritis)
When psoriasis affects more than 10% of the body or involves the joints (Psoriatic Arthritis), oral or injectable drugs are prescribed.
A. Immunosuppressants
- Methotrexate: Suppresses T-cell activity, but causes liver toxicity.
- Cyclosporine: Strong immunosuppressant; used for short-term flare-ups.
B. Biologic Therapies (Targeted Immune Modulators)
- TNF-α inhibitors: Infliximab, Adalimumab, Etanercept.
- IL-17 inhibitors: Secukinumab, Ixekizumab.
- IL-23 inhibitors: Guselkumab, Tildrakizumab.
- JAK inhibitors: Tofacitinib (for psoriatic arthritis).
- Mechanism: Blocks specific immune pathways involved in psoriasis.
- Side Effects: Risk of infections (TB, fungal infections), increased cancer risk, liver damage.
C. Oral Retinoids (For Severe Psoriasis)
- Acitretin: Helps normalize skin cell production but has teratogenic effects (birth defects).
4. Lifestyle Modifications
- Anti-inflammatory diet: Rich in omega-3s (fish, flaxseeds), leafy greens, turmeric.
- Weight management: Reduces systemic inflammation.
- Stress management: Meditation, yoga, and cognitive therapy.
- Avoid alcohol & smoking: Reduces flare-ups.
Ayurvedic Treatment for Psoriasis (Ekakushta & Kitibha)
Ayurveda treats psoriasis by detoxifying the body, balancing the doshas, and restoring digestion (Agni).
1. Panchakarma (Detoxification Therapy for Severe Psoriasis)
Ayurvedic detox therapy eliminates accumulated toxins (Ama) and balances Vata-Pitta-Kapha.
A. Vamana (Therapeutic Emesis) – Kapha Detox
- Used for Kapha-dominant psoriasis (thick, oozing lesions).
- Method: Herbal decoctions like Madanaphala (Randia dumetorum) induce vomiting.
- Effect: Cleanses upper GI tract and skin.
B. Virechana (Purgation Therapy) – Pitta Detox
- Used for Pitta-dominant psoriasis (red, inflamed lesions).
- Herbs used: Trivrit (Operculina turpethum), Avipattikar Churna.
- Effect: Removes excess heat and toxins from the liver & intestines.
C. Rakta Mokshana (Bloodletting Therapy) – Toxin Removal
- Leech Therapy (Jalaukavacharana) for severe, chronic psoriasis.
- Effect: Removes inflammatory mediators from the blood.
D. Basti (Medicated Enema) – Vata Balance
- Used for dry, cracked psoriasis lesions.
- Medicated Oils: Dashamoola, Bala, and Triphala-based Basti.
2. Internal Ayurvedic Medicines for Psoriasis
| Ayurvedic Medicine | Properties |
|---|---|
| Mahamanjishthadi Kwath | Blood purifier, anti-inflammatory |
| Kaishore Guggulu | Detoxifies liver and reduces inflammation |
| Arogyavardhini Vati | Balances digestion, clears Ama (toxins) |
| Haridra (Turmeric) | Contains curcumin, anti-inflammatory |
| Neem (Azadirachta indica) | Antibacterial, blood purifier |
| Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia) | Enhances immunity and skin health |
| Chandraprabha Vati | Detoxifies the urinary tract, reduces Kapha |
3. External Ayurvedic Therapies (Lepa & Abhyanga)
- Neem & Turmeric Paste: Anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial.
- Aloe Vera Gel: Hydrates and soothes inflamed skin.
- Karanja (Pongamia pinnata) Oil: Reduces thick plaques.
- Takra Dhara (Butter Milk Therapy): Cooling therapy for Pitta psoriasis.
4. Ayurvedic Diet (Pathya & Apathya for Psoriasis)
- Recommended Foods (Pathya):
- Bitter vegetables: Bitter gourd, neem leaves.
- Herbal teas: Turmeric, licorice, ginger tea.
- Buttermilk and coconut water.
- Whole grains like barley and millets.
- Foods to Avoid (Apathya):
- Dairy products, red meat, sour foods.
- Alcohol, processed foods, and excessive salt.
5. Lifestyle Modifications (Vihara) in Ayurveda
- Daily Abhyanga (Self-massage) with medicated oils like Mahamarichyadi Taila.
- Yoga & Meditation to balance doshas (Shavasana, Anulom-Vilom).
- Avoid exposure to cold and dry weather.
- Regular sun exposure (10–15 min/day) to improve Vitamin D levels naturally.
Conclusion
Modern medicine offers effective symptom management, but biologic drugs, steroids, and immunosuppressants carry risks. Ayurveda, on the other hand, targets the root cause through detoxification, dietary corrections, and herbal treatments. A holistic approach combining both systems can offer sustainable relief and improve the quality of life for psoriasis patients.
References
- Challenges and Future Trends in the Treatment of Psoriasis
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10487560/ - Psoriasis: A Brief Overview
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8140694/ - Pathophysiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Psoriasis
https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2766169 - Inflammation and Psoriasis: A Comprehensive Review
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/24/22/16095 - Psoriasis and Molecular Target Therapies: Evidence of Efficacy in Real-Life Practice
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40257-023-00798-5
Other articles :
- Global Perspectives on Folliculitis: Ayurveda’s Approach to Prevention, Treatment, and Healthcare Disparities
- How to Lose Weight in 1 Week: Ayurvedic and Research-Based Insights
- 50 Research Paper Insights into Sleep: The Ultimate Guide to Health, Cognitive Performance, and Longevity
- Top 20 Most comely Useful Instruments in Physiology lab with their classification- part 4
- BEST AYURVEDIC DIET AND NUTRITION GUIDE
- AYURVEDA INTRODUCTION
- Growth of the Ayurveda Wellness Market in 2024: Personalization, Technology, and Global Expansion
- Shat Kriyakala: Understanding 6 Stage of Disease Progression in Ayurveda and Its Modern Relevance
- Understanding Concepts 3 Doshas in Ayurveda: Tridosha
- Anatomy, Function, and Clinical Insights into the Mediastinum: A Comprehensive Overview
- Stress Relief and Mental Wellness: Understanding Causes, Effects and Effective Strategies
- Arthritis explore Ayurvedic and Modern Aspects
- Over view of the Urinary System: Embryology , Functions and Congenital Diseases
- Understanding Of Renal Agenesis : Symptoms , Causes , Diagnosis and Treatment
- Avascular Necrosis (AVN) of the Hip







Pingback: The Real Causes of Acne Vulgaris: Science-Backed Explanation -
Pingback: Acne Vulgaris: Diagnostic Aspects and Clinical Assessment – An Integrative Ayurvedic and Modern Perspective -