TABLE OF CONTENT
Table of Contents
- TABLE OF CONTENT
- 1. Microscope:
- 2. Spirometer :
- 3. Electrocardiograph (ECG) Machine :
- 4. Sphygmomanometer :
- 5. Spectrophotometer:
- 6. Centrifuge :
- 7. Polygraph :
- 8. pH Meter :
- 9. Blood Glucose Meter :
- 10. Oscilloscope :
Here is a list of most important instruments commonly used in physiology labs, along with a brief description for each
1. Microscope:
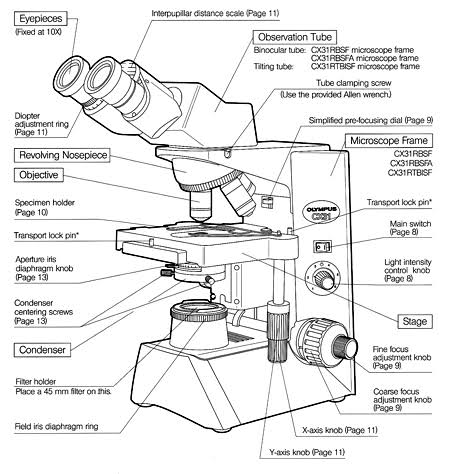
A microscope is an instrument used to magnify and view objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. There are several types of microscopes:
- Light Microscope: Uses visible light to magnify objects, commonly used in biology labs.
- Electron Microscope: Uses beams of electrons for greater magnification and resolution, ideal for viewing ultra-small structures like cells and viruses.
- Fluorescence Microscope: Uses fluorescence and phosphorescence to study specimens tagged with fluorescent dyes.
- Scanning Probe Microscope: Uses a physical probe to scan the specimen, offering detailed surface imaging.
2. Spirometer :
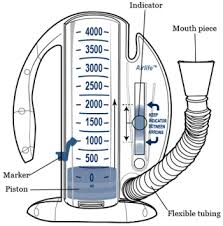
A spirometer is a device used to measure lung function, specifically the volume of air inhaled and exhaled. It helps diagnose and monitor respiratory conditions.
Types of spirometers include:
- Volume Spirometer: Measures the total amount of air exhaled or inhaled.
- Flow Spirometer: Measures the flow rate of air during respiration.
- Incentive Spirometer: Used to encourage deep breathing, often for postoperative patients to prevent lung complications.
3. Electrocardiograph (ECG) Machine :
An ECG (Electrocardiogram) is a medical test that records the electrical activity of the heart to detect abnormalities. It helps diagnose heart conditions such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, and other cardiac issues.
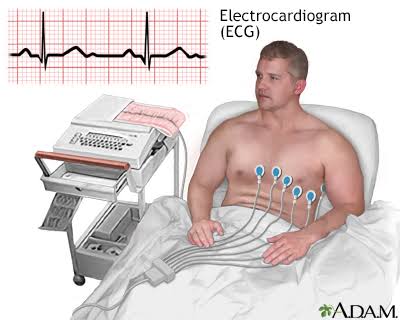
Types of ECG include:
- Resting ECG: Performed while the patient is at rest to check the heart’s electrical activity.
- Stress ECG: Conducted during physical activity to observe heart function under stress.
- Holter Monitor: A portable ECG device worn over 24-48 hours to monitor heart activity continuously.
- Event Monitor: Worn for longer periods, it records only when the patient experiences symptoms.
4. Sphygmomanometer :
A sphygmomanometer is a device used to measure blood pressure, which helps assess cardiovascular health. It consists of a cuff, a measuring unit, and often a stethoscope to listen to blood flow.
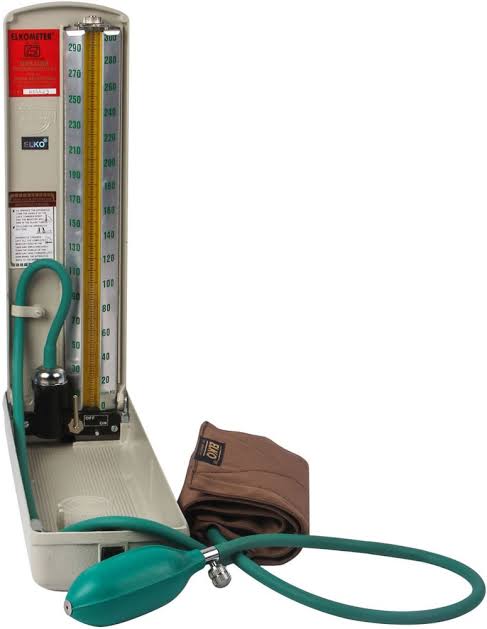

Types of sphygmomanometers include:
- Mercury Sphygmomanometer: Uses mercury columns for accurate pressure readings.
- Aneroid Sphygmomanometer: Uses a mechanical dial and is more portable than mercury types.
- Digital Sphygmomanometer: Uses electronic sensors and displays readings on a digital screen for ease of use.
5. Spectrophotometer:
A spectrophotometer is an analytical instrument used to measure the intensity of light absorbed by a solution at different wavelengths. It is commonly used in chemistry, biology, and medical labs for quantitative analysis of substances.
Types of spectrophotometers include:
- UV-Vis Spectrophotometer: Measures absorbance in the ultraviolet and visible light range.
- Infrared (IR) Spectrophotometer: Measures absorbance in the infrared range, often used for organic compounds.
- Flame Photometer: Measures the intensity of light emitted by a sample when it’s introduced into a flame, used for detecting metal ions.
- Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer: Measures the concentration of elements in a sample by absorbing specific wavelengths of light.
6. Centrifuge :
A centrifuge is a device used to separate substances of different densities in a liquid by spinning them at high speeds. It is widely used in laboratories for separating components like cells, proteins, or chemicals.
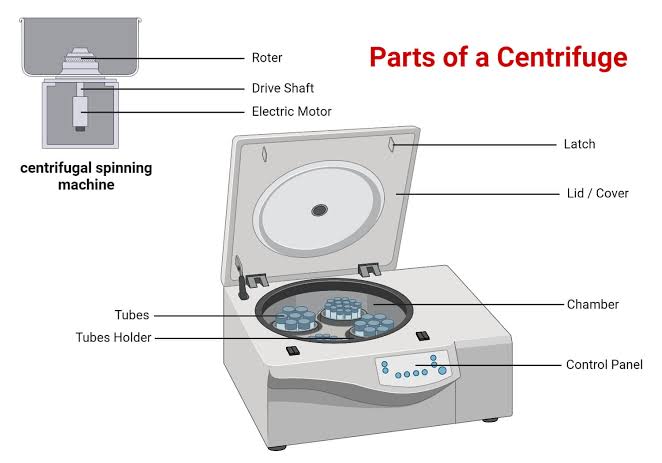
Types of centrifuges include:
- Microcentrifuge: Used for small-volume samples, typically in molecular biology.
- Clinical Centrifuge: Common in medical labs for blood or urine sample separation.
- Ultracentrifuge: Operates at very high speeds for separating very small particles, such as viruses or proteins.
- Refrigerated Centrifuge: Maintains low temperatures to prevent sample degradation during the process.
7. Polygraph :
A polygraph, commonly known as a lie detector, is a device that measures physiological responses such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiration, and skin conductivity to determine if a person is being deceptive.
Types of polygraphs include:
- Analog Polygraph: Uses mechanical devices to record physiological responses on paper.
- Digital Polygraph: Records and displays physiological responses electronically, often with advanced software for analysis.
- Computerized Polygraph: Combines digital recording with computer software to enhance data analysis and interpretation.
8. pH Meter :
A pH meter is an instrument used to measure the acidity or alkalinity of a solution by detecting its hydrogen ion concentration. It is commonly used in laboratories, agriculture, and water testing.

Types of pH meters include:
Continuous pH Meter: Monitors pH levels in real-time, often used in industrial processes.
Benchtop pH Meter: Stationary and highly accurate, used in labs for precise measurements.
Portable pH Meter: Lightweight and battery-powered, ideal for fieldwork and on-site testing.
Pen pH Meter: Compact and easy to use, suitable for quick and general pH measurements.
9. Blood Glucose Meter :
A blood glucose meter is a medical device used to measure the concentration of glucose in the blood, helping individuals with diabetes monitor and manage their blood sugar levels.
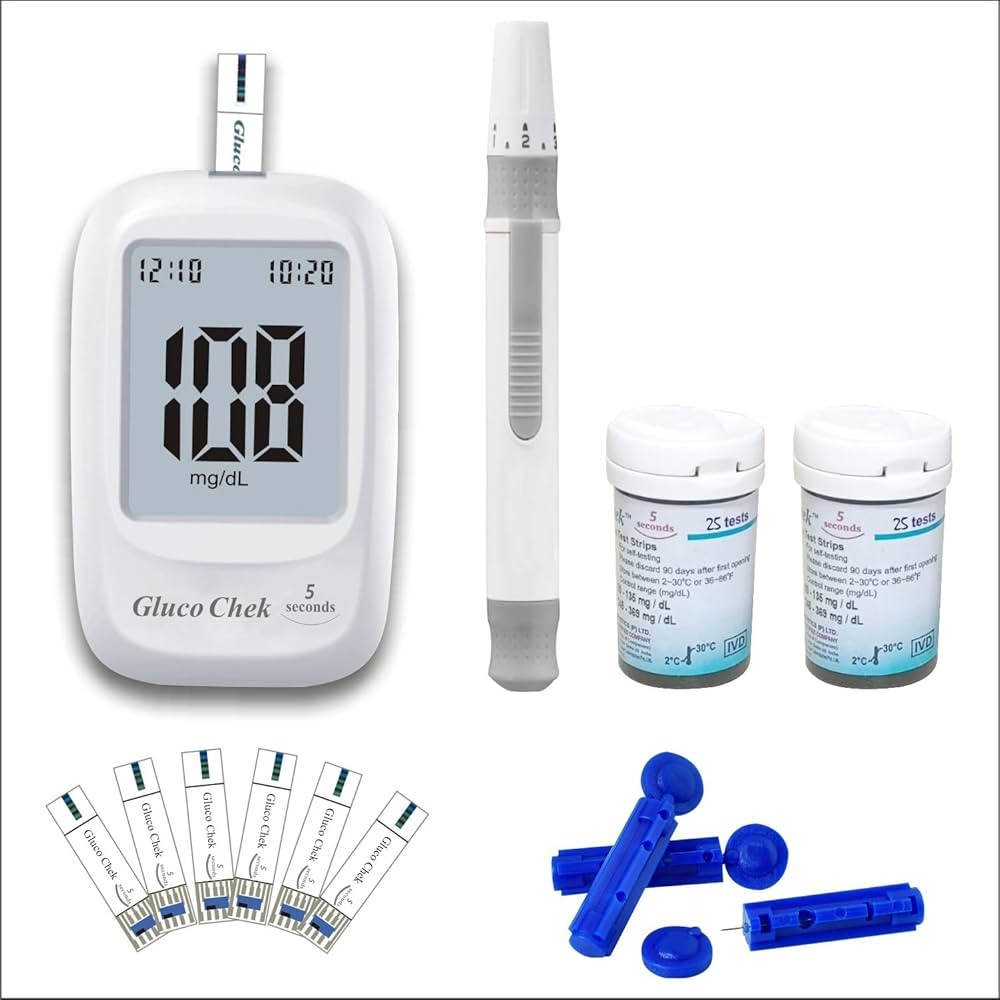
Types of blood glucose meters include:
Talking Glucose Meter: Designed for visually impaired individuals, providing audio readings of blood glucose levels.
Standard Glucose Meter: Requires a blood sample from a finger prick, providing quick readings.
Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM): Worn on the body, it continuously tracks glucose levels and alerts users of highs and lows.
Flash Glucose Monitor: Allows users to scan a sensor on the skin for real-time glucose readings without constant finger pricks.
10. Oscilloscope :
An oscilloscope is an electronic instrument used to visualize and analyze the varying voltage signals over time. It is essential for testing, debugging, and designing electrical circuits by providing real-time waveform analysis.
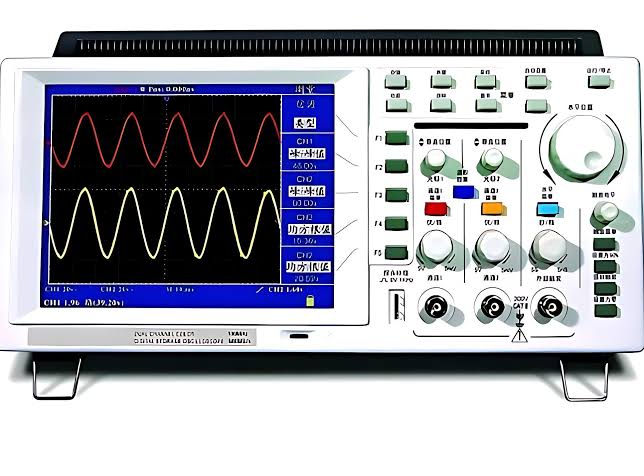
Types of oscilloscopes include:
- Analog Oscilloscope: Displays signals directly using electron beams, offering real-time visualization with minimal processing delay.
- Digital Storage Oscilloscope (DSO): Converts analog signals to digital form, allowing for signal capture, storage, and detailed analysis.
- Mixed-Signal Oscilloscope (MSO): Combines analog and digital signal analysis, useful in systems where both types of signals interact.
- Digital Phosphor Oscilloscope (DPO): Offers high-speed waveform capture and advanced visual representation of signal changes.
- Handheld Oscilloscope: Portable version, used in field testing and on-site diagnostics with compact, battery-operated functionality.
If you have any queries regarding this article reach us @globeayush-com







Pingback: Top 10 Most Useful Instruments in Physiology- Part 2 - GlobeAyush
Pingback: Top 10 Most Useful Instruments in Physiology- Part 3 - GlobeAyush
Pingback: Top 20 Most comely Useful Instruments in Physiology lab with their classification- part 4 - GlobeAyush
Pingback: 5000 Year Old Great Ayurvedic dermatology - GlobeAyush
Pingback: Growth of the Ayurveda Wellness Market in 2024: Personalization, Technology, and Global Expansion - GlobeAyush
Pingback: Best 13 Types of Abhyanga With Morden Research & Classical Ayurvedic Texts - GlobeAyush
Pingback: 10 Powerful Health Benefits of Tulsi: Ayurveda’s Miracle Herb for Immunity and Wellness - GlobeAyush
Pingback: 50 Research Paper Insights into Sleep: The Ultimate Guide to Health, Cognitive Performance, and Longevity - GlobeAyush