Table of Contents
- 1. Treadmill Machine
- 2. Metronome :
- 3. Calorimeter :
- 4. Stethoscope :
- 5. Thermometer :
- 6. Pulse Oximeter :
- 7. Goniometer :
- 8. Galvanometer :
- 9. Manometer :
- 10. Biopac System :
1. Treadmill Machine
Introduction: A treadmill is a device used for walking, running, or climbing while staying in the same place. It is commonly used for cardiovascular exercise and fitness training.
Major Classification:

- Manual Treadmills: Powered by the user’s movement.
Example: Sunny Health & Fitness Manual Treadmill. - Motorized Treadmills: Powered by an electric motor, allowing speed adjustments.
Example: NordicTrack T Series Treadmill. - Folding Treadmills: Designed for easy storage, with foldable frames.
Example: XTERRA Fitness TR150.
2. Metronome :
Introduction: A metronome is a device used by musicians to keep a steady tempo by producing regular, metrical ticks or beats.

Major Classification:
- Mechanical Metronomes: Powered by a wind-up mechanism.
Example: Wittner 903 Double Bell Metronome. - Digital Metronomes: Powered by electricity or batteries with more features.
Example: Korg MA-2 Digital Metronome. - Software Metronomes: Available as apps or computer programs.
Example: Metronome Beats (app).
3. Calorimeter :
Introduction: A calorimeter is a device used to measure the heat involved in chemical reactions or physical changes.
Major Classification:
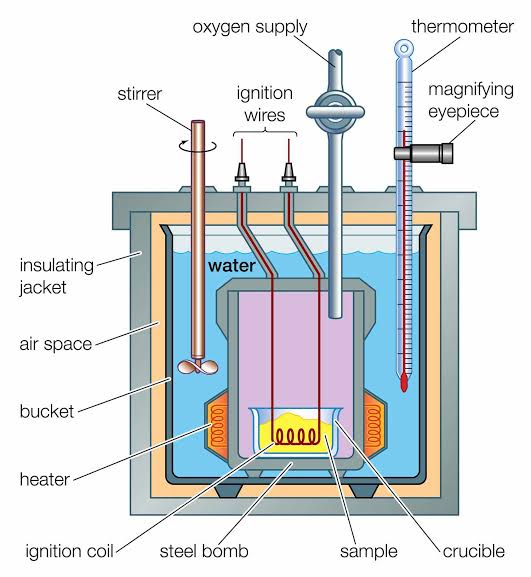
- Bomb Calorimeter: Used to measure the heat of combustion.
Example: Parr 6400 Calorimeter. - Differential Scanning Calorimeter (DSC): Measures heat flow associated with phase transitions.
Example: TA Instruments DSC 250. - Solution Calorimeter: Used to measure heat changes in a solution.
Example: ThermoFluor Calorimeter.
4. Stethoscope :
Introduction: A stethoscope is a medical device used to listen to internal sounds of the body, such as the heartbeat and lungs.
Major Classification:

- Acoustic Stethoscope: Traditional type, relies on sound waves.
Example: 3M Littmann Classic III. - Electronic Stethoscope: Amplifies body sounds for better clarity.
Example: Eko Core Digital Stethoscope. - Fetal Stethoscope: Used to monitor fetal heartbeat.
Example: Pinnard Stethoscope.
5. Thermometer :
Introduction: A thermometer is an instrument used to measure temperature.
Major Classification:
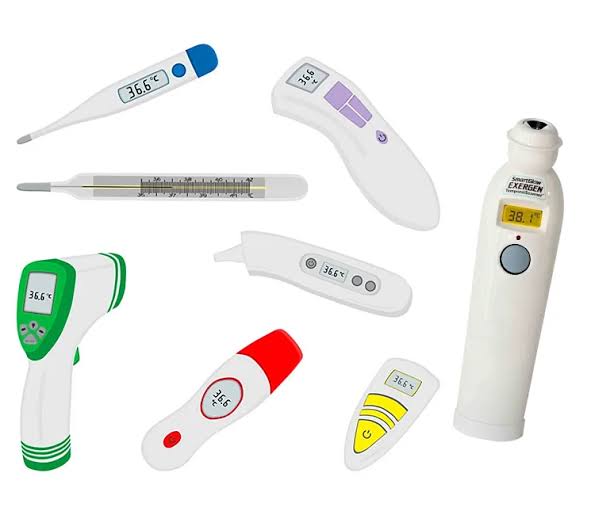
- Mercury Thermometers: Traditional thermometer using mercury in a glass tube.
Example: Geratherm Classic Thermometer. - Digital Thermometers: Provide electronic readings.
Example: Braun Digital Thermometer. - Infrared Thermometers: Measure temperature without contact using infrared radiation.
Example: iHealth No-Touch Forehead Thermometer.
6. Pulse Oximeter :
Introduction: A pulse oximeter is a device that measures the oxygen saturation level of the blood and pulse rate.
Major Classification:
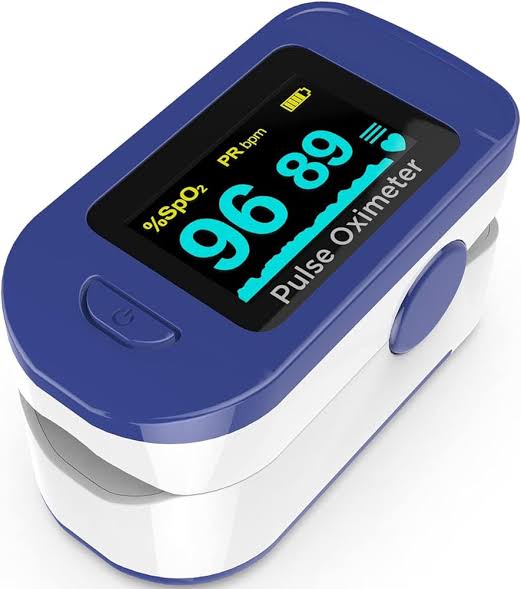
- Fingertip Pulse Oximeter: Clips onto a finger to measure oxygen levels.
Example: Zacurate Pro Series 500DL. - Handheld Pulse Oximeter: Portable device with a probe for monitoring.
Example: Contec CMS50D+. - Wrist Pulse Oximeter: Worn on the wrist for continuous monitoring.
Example: Viatom Wearable Pulse Oximeter.
7. Goniometer :
Introduction: A goniometer is a device used to measure angles or the range of motion in joints.
Major Classification:

- Universal Goniometer: Manual device with a protractor-style design.
Example: Baseline Plastic Goniometer. - Digital Goniometer: Provides electronic angle measurements.
Example: Halo Digital Goniometer. - Electrogoniometer: Used for more complex biomechanical analysis.
Example: Biometrics SG Series.
8. Galvanometer :
Introduction: A galvanometer is an instrument used for detecting and measuring electric current.
Major Classification:
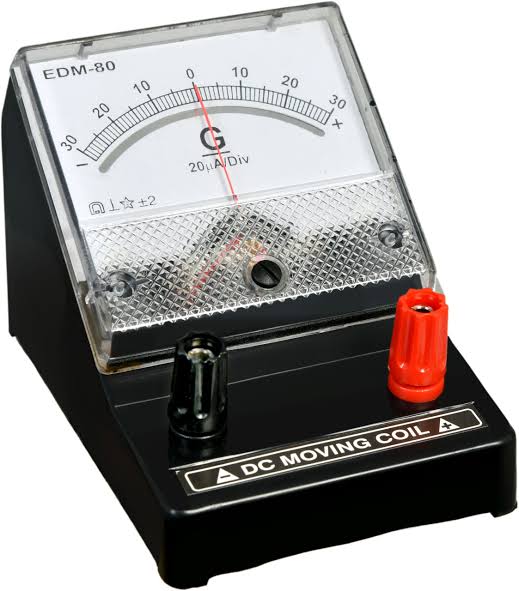

- Moving Coil Galvanometer: Uses a coil suspended in a magnetic field.
Example: Weston Moving Coil Galvanometer. - Ballistic Galvanometer: Measures charge rather than current.
Example: PASCO SE-8658 Ballistic Galvanometer. - Vibration Galvanometer: Used in high-frequency AC circuits.
Example: D’Arsonval Galvanometer.
Detects small electrical currents, used in electrophysiology.
9. Manometer :
Introduction: A manometer is used to measure the pressure of gases or liquids.
Major Classification:
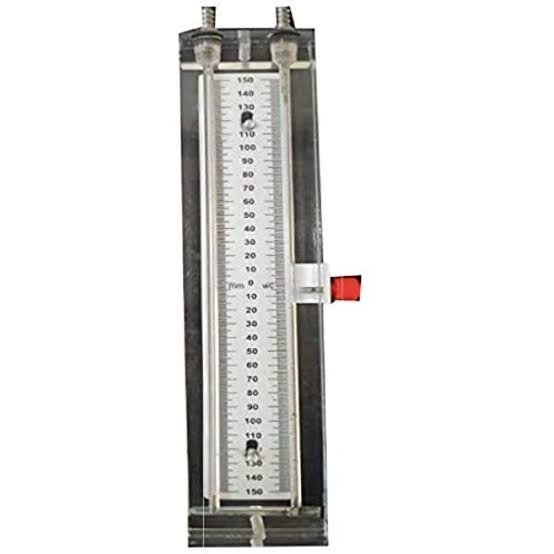

- U-Tube Manometer: Consists of a U-shaped tube filled with liquid.
Example: DWYER Mark II Manometer. - Digital Manometer: Displays pressure measurements electronically.
Example: Extech HD755 Digital Manometer. - Inclined Manometer: Used for measuring low pressures.
Example: Dwyer 475-1 Inclined Manometer.
10. Biopac System :
Introduction: The Biopac system is a comprehensive physiological data acquisition and analysis tool used in research and education.
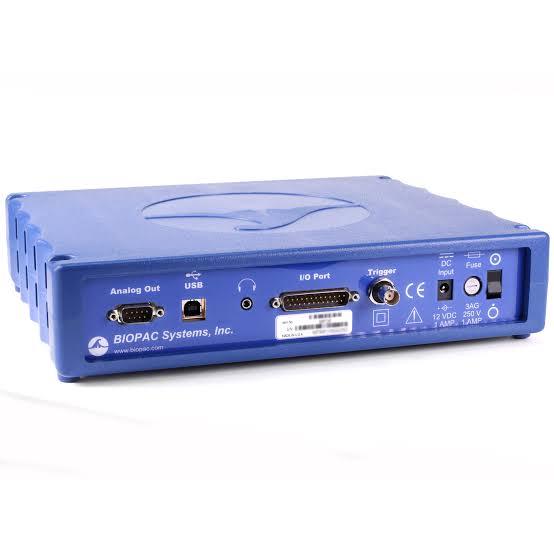

Major Classification:
- MP System: Modular platform for collecting physiological data.
Example: MP160 Data Acquisition System. - BioNomadix: Wireless system for real-time data collection.
Example: BioNomadix Wireless System. - B-Alert X10: Wireless EEG system for brain monitoring.
Example: B-Alert X10 System.
Used for recording and analyzing physiological signals.
For other physiology instruments visit our part 1 post
If you have any queries regarding this article reach us @globeayush-com and Click here for Contact us







Pingback: Top 20 Most comely Useful Instruments in Physiology lab with their classification- part 4 - GlobeAyush
Pingback: Best 13 Types of Abhyanga With Morden Research & Classical Ayurvedic Texts - GlobeAyush