Table of Contents
- 1. Audiometer :
- 2. Refractometer :
- 3. Flow Cytometer :
- 4. Hemocytometer :
- 5. Pulse Transducer :
- 6. Optometer :
- 7. Urinalysis Strips :
- 8. Defibrillator :
- 9.Glucometer :
- 10. Heart Rate Monitor :
- Other link
1. Audiometer :
An audiometer is an instrument used to measure hearing acuity. It generates sounds at various frequencies and intensities to determine hearing thresholds.
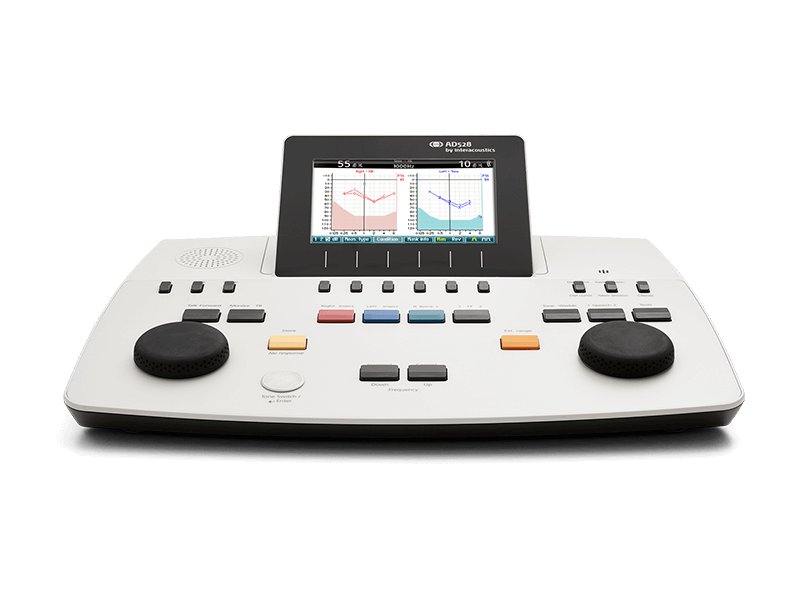

Classification:
- Clinical Audiometer (used in diagnostic settings)
- Screening Audiometer (for quick hearing tests)
Example: Pure-tone audiometer.
2. Refractometer :
A refractometer measures the refractive index of a substance, often used to determine the concentration of solutes in a liquid.
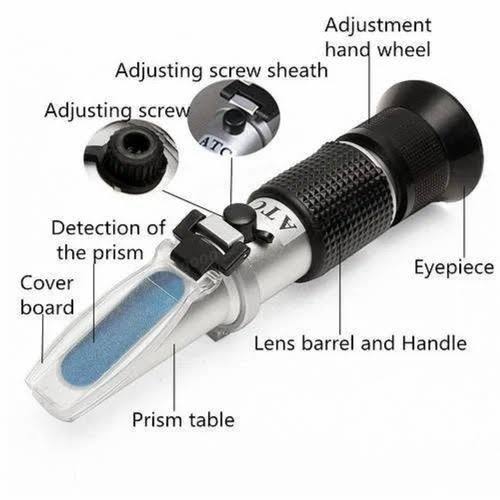

Classification:
- Handheld Refractometer (portable)
- Digital Refractometer (automated)
Example: Urine refractometer for checking hydration.
3. Flow Cytometer :
Flow cytometers are used to analyze the physical and chemical characteristics of cells or particles as they pass through a laser beam.
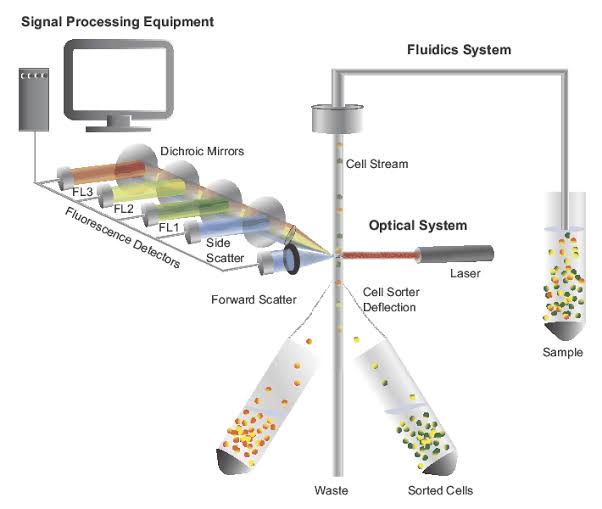
Classification:
- Sorting Flow Cytometer (used for separating cell types)
- Example: FACS (Fluorescence-activated cell sorting).
4. Hemocytometer :
A hemocytometer is a device used to manually count cells, such as blood cells, in a defined volume of fluid.
Classification:

- Standard Hemocytometer (for general cell counting)
- Improved Neubauer Hemocytometer (enhanced accuracy)
Example: Counting red and white blood cells in blood samples.
5. Pulse Transducer :
A pulse transducer measures the pulse rate by detecting changes in blood volume in arteries.
Classification:
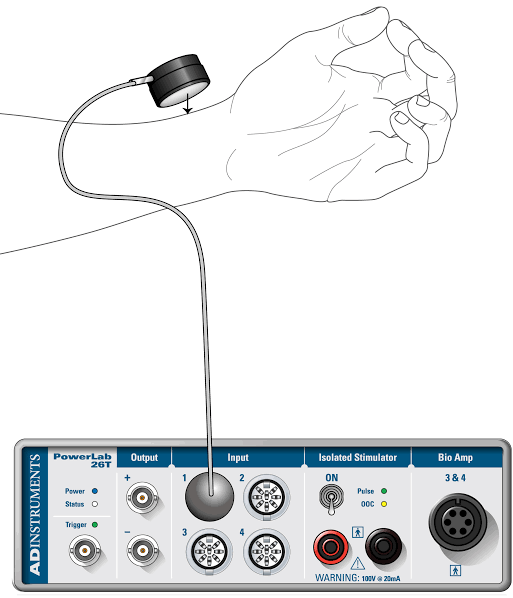
- Photoplethysmography (PPG) Transducer (uses light).
- Pressure Pulse Transducer (measures mechanical pressure)
- Example: Finger pulse transducer.
6. Optometer :
An optometer measures the refractive power of the eye, helping to assess vision correction needs.
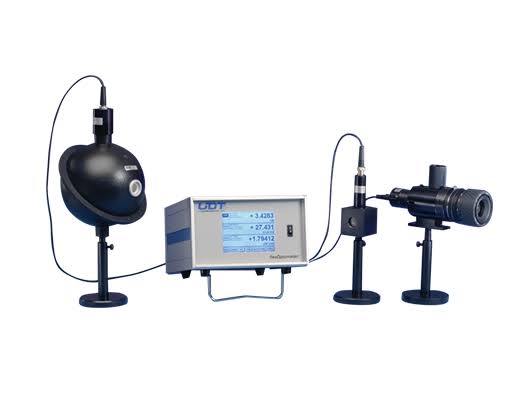

Classification:
- Manual Optometer (requires manual adjustment)
- Automated Optometer (automated readings)
Example: Autorefractor used in eye exam
7. Urinalysis Strips :
Urinalysis strips are diagnostic tools used to detect substances in urine, such as glucose, protein, or pH levels.
Classification:
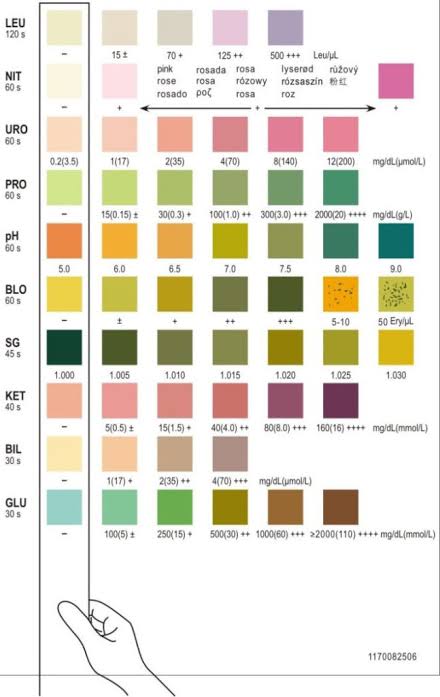
- Multistix (measures multiple parameters)
- Single Analyte Strips (measures one parameter)
Example: Ketone testing strips for diabetics.
8. Defibrillator :
A defibrillator delivers a dose of electric current to the heart to restore a normal rhythm.
Classification:
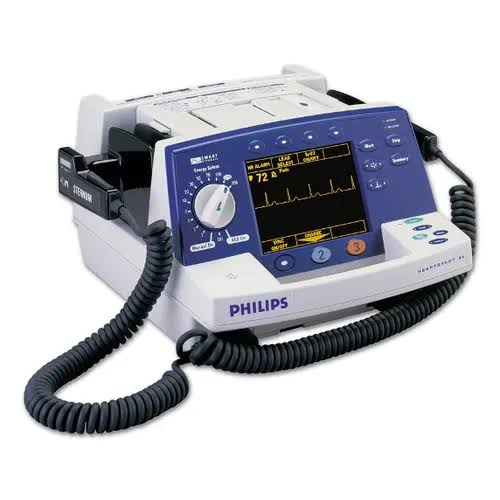
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD)
Example: AED used in emergency cardiac arrest.
9.Glucometer :
A glucometer measures blood glucose levels, commonly used by diabetics for monitoring.
Classification:
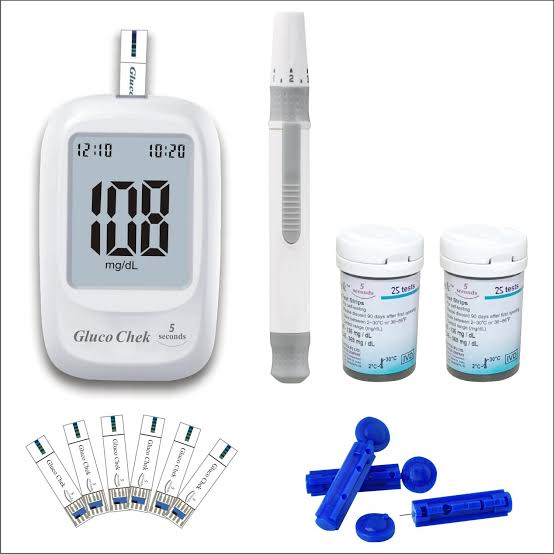
- Invasive Glucometer (requires blood sample)
- Non-invasive Glucometer (uses alternative methods like infrared)
Example: Finger-prick glucometer.
10. Heart Rate Monitor :
A heart rate monitor tracks heart rate, either continuously or on-demand, often used in fitness and medical settings.

Classification:
- Chest Strap Heart Rate Monitor (measures electrical signals)
- Wrist-Based Optical Heart Rate Monitor (uses light sensors)
Example: Smartwatches with heart rate monitoring function.
Tracks heart rate in real-time
Other link
- Top 10 Most Useful Instruments in Physiology- Part 1
- Top 10 Most Useful Instruments in Physiology- Part 2
- BEST AYURVEDIC DIET AND NUTRITION GUIDE
If you have any queries regarding this article reach us @globeayush-com and Contact us






Pingback: Best 13 Types of Abhyanga With Morden Research & Classical Ayurvedic Texts - GlobeAyush